Understanding Convertible Bonds: A Hybrid Investment
What is a Convertible Bond?
A convertible bond is a type of debt security that offers investors a unique blend of fixed-income and equity features. It combines the characteristics of both bonds and stocks, providing investors with potential upside while mitigating downside risk.
Key Features of Convertible Bonds
- Fixed-Income Component: Like traditional bonds, convertible bonds pay periodic interest payments to investors at a fixed rate.
- Equity Component: The bondholder has the option to convert the bond into a specified number of common shares of the issuing company. This conversion feature gives investors the potential to participate in the company's future growth.
Why Choose Convertible Bonds?
Convertible bonds offer several advantages to investors:
- Potential for Capital Appreciation: If the company's stock price rises significantly, the convertible bondholder can convert their bond into shares, capturing the upside potential.
- Lower Interest Rates: Due to the conversion option, issuers can often offer lower interest rates on convertible bonds compared to traditional bonds.
- Downside Protection: In the event of a decline in the company's stock price, the bondholder can retain the bond's fixed-income features, limiting potential losses.
- Tax Advantages: In some jurisdictions, interest payments on convertible bonds may be tax-deductible for the issuer, making them an attractive financing option.
How Convertible Bonds Work
- Issuance: A company issues convertible bonds to raise capital.
- Interest Payments: The bondholder receives periodic interest payments at a fixed rate.
- Conversion Option: The bondholder has the right to convert the bond into a specified number of common shares at a predetermined conversion price.
- Conversion Trigger: The bondholder may choose to convert the bond when the market price of the stock exceeds the conversion price.
- Maturity: If the bondholder does not convert the bond, it matures at a specified date, and the issuer repays the principal amount.
Example of a Convertible Bond
Suppose Company XYZ issues a convertible bond with a face value of $1,000, a 5% annual interest rate, and a conversion price of $25 per share. If the stock price of Company XYZ rises to $30 per share, the bondholder can convert the bond into 40 shares ($1,000 / $25).
Convertible Bond vs. Traditional Bond
| Feature | Convertible Bond | Traditional Bond |
|---|---|---|
| Interest Payments | Fixed interest payments | Fixed interest payments |
| Principal Repayment | At maturity or upon conversion | At maturity |
| Equity Upside | Potential to convert into shares | No equity upside |
| Risk Profile | Lower interest rate but higher risk | Higher interest rate but lower risk |
In Conclusion
Convertible bonds offer a unique investment opportunity that combines the stability of fixed-income investments with the growth potential of equities. By understanding the key features and benefits of convertible bonds, investors can make informed decisions about incorporating them into their investment portfolios.
Note: Investing in convertible bonds involves risks, including the risk of default by the issuer and fluctuations in the underlying stock price. It is important to conduct thorough research and consider consulting with a financial advisor before making any investment decisions.
Types of Convertible Bonds
Convertible bonds offer a hybrid investment opportunity, combining the features of both debt and equity. Here are the primary types of convertible bonds:
| Type of Convertible Bond | Description |
|---|---|
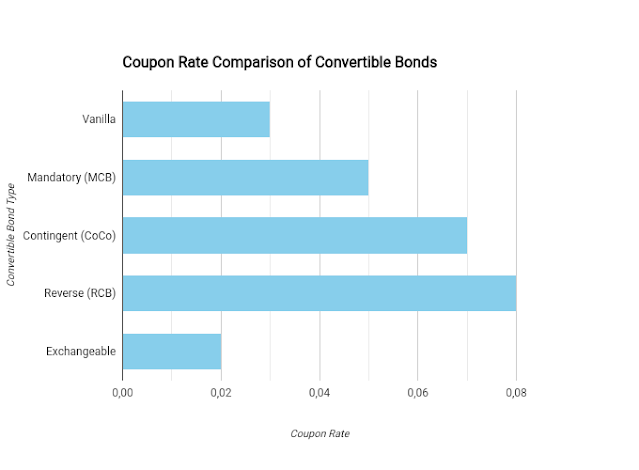
| Vanilla Convertible Bond | The most common type. Offers the right to convert the bond into a specified number of shares at a predetermined conversion price. |
| Mandatory Convertible Bond | Requires the bondholder to convert the bond into shares at a specific date, usually at maturity. |
| Contingent Convertible Bond (CoCo) | Also known as a "convertible contingent bond," it automatically converts to equity under specific conditions, such as when the issuer's capital falls below a certain threshold. |
| Reverse Convertible Bond | A structured product that offers a higher coupon rate but carries the risk of loss if the underlying asset's price falls below a certain level. |
| Exchangeable Bond | Similar to a convertible bond, but allows the bondholder to exchange the bond for shares of a different company, typically a subsidiary or a related entity. |
Key Considerations for Investors:
- Conversion Price: The price at which the bond can be converted into shares.
- Conversion Ratio: The number of shares received for each bond.
- Conversion Premium: The difference between the conversion price and the market price of the underlying stock.
- Call Feature: The issuer's right to redeem the bond before maturity.
- Put Feature: The bondholder's right to sell the bond back to the issuer before maturity.
Investing in Convertible Bonds
Convertible bonds can be a valuable tool for investors seeking a mix of income and growth. However, it's essential to understand the risks and rewards associated with these complex instruments. Consider consulting with a financial advisor to determine if convertible bonds are suitable for your investment goals and risk tolerance.
Note: The specific terms and conditions of convertible bonds can vary widely, so it's crucial to carefully review the offering documents before investing.
Vanilla Convertible Bond: A Comprehensive Guide
A vanilla convertible bond is a type of debt security that offers the holder the option to convert the bond into a specified number of common shares of the issuing company. It combines the features of both a traditional bond and a stock option.
Key Features of a Vanilla Convertible Bond:
- Face Value: The nominal value of the bond, typically $1,000.
- Coupon Rate: The interest rate paid on the bond, usually fixed.
- Maturity Date: The date on which the bond matures and the principal is repaid.
- Conversion Ratio: The number of shares into which each bond can be converted.
- Conversion Price: The price per share implied by the conversion ratio.
- Call Provision: The issuer's right to redeem the bonds before maturity.
- Put Provision: The bondholder's right to force the issuer to redeem the bonds before maturity.
Example of a Vanilla Convertible Bond
Let's consider a hypothetical vanilla convertible bond issued by Company XYZ:
| Feature | Value |
|---|---|
| Face Value | $1,000 |
| Coupon Rate | 5% |
| Maturity Date | 5 years |
| Conversion Ratio | 20 shares |
| Conversion Price | $50 ($1,000 / 20) |
| Call Provision | Yes, at a premium |
| Put Provision | No |
How a Vanilla Convertible Bond Works
- Interest Payments: The bondholder receives periodic interest payments based on the coupon rate.
- Principal Repayment: At maturity, the bondholder receives the face value of the bond.
- Conversion Option: The bondholder can choose to convert the bond into shares at any time before the maturity date. The number of shares received is determined by the conversion ratio.
- Call Feature: The issuer can call the bond before maturity, forcing the bondholder to either convert or receive the call price.
- Put Feature: If the bond has a put feature, the bondholder can force the issuer to redeem the bond before maturity.
Advantages of Vanilla Convertible Bonds
- Potential for Capital Appreciation: If the stock price rises above the conversion price, the bondholder can convert the bond into shares and benefit from the stock's upside potential.
- Lower Interest Rate: Convertible bonds often have lower interest rates than traditional bonds due to the conversion option.
- Hybrid Security: It offers a combination of fixed-income and equity features.
- Protection Against Downside Risk: In a declining market, the bondholder can hold the bond to maturity and receive the face value.
Disadvantages of Vanilla Convertible Bonds
- Dilution Risk: If the company issues more shares, the value of existing shares, including those obtained through conversion, may decrease.
- Limited Upside Potential: The upside potential is capped by the conversion price.
- Credit Risk: If the issuer defaults, the bondholder may lose their investment.
Conclusion
Vanilla convertible bonds offer a unique investment opportunity for investors seeking a blend of fixed-income and equity characteristics. By understanding the key features and risks, investors can make informed decisions about whether to invest in these securities.
Mandatory Convertible Bond
A Mandatory Convertible Bond (MCB) is a type of debt security that is automatically converted into common stock on a predetermined date, typically at maturity. Unlike traditional convertible bonds, where the conversion decision rests with the bondholder, MCBs offer no such choice.
Key Features of a Mandatory Convertible Bond
| Feature | |
|---|---|
| Mandatory Conversion: The bondholder is obligated to convert the bond into common stock on a specific date, usually the maturity date. | |
| Conversion Ratio: This determines the number of shares into which each bond will be converted. | |
| Conversion Price: The price per share implied by the conversion ratio. | |
| Yield: MCBs often offer higher yields than traditional bonds to compensate for the lack of conversion flexibility. |
How a Mandatory Convertible Bond Works
- Issuance: The company issues the MCBs to raise capital.
- Interest Payments: During the bond's life, the issuer pays periodic interest payments to the bondholders.
- Mandatory Conversion: On the specified conversion date, the bondholder's position automatically converts into common stock.
Advantages of Mandatory Convertible Bonds
- Enhanced Yield: MCBs often offer higher yields than traditional bonds to compensate for the mandatory conversion feature.
- Equity Upside: Investors can participate in the potential upside of the company's stock price.
- Reduced Credit Risk: As the bondholder is eventually converted into a shareholder, the credit risk associated with the bond is mitigated.
Disadvantages of Mandatory Convertible Bonds
- Lack of Flexibility: Bondholders have no option to choose the timing of conversion, which may not be ideal if the stock price is low at the conversion date.
- Dilution Risk: The conversion of bonds into shares can dilute the value of existing shares.
Use Cases of Mandatory Convertible Bonds
- Raising Capital: Companies often use MCBs to raise capital, especially when they expect future growth and want to reward investors with equity upside.
- Debt Refinancing: MCBs can be used to refinance existing debt, reducing interest costs and extending the maturity profile.
- Strategic Partnerships: MCBs can be issued to strategic partners as a form of equity-linked compensation.
In Conclusion
Mandatory Convertible Bonds offer a unique blend of debt and equity features. While they provide a higher yield and potential equity upside, they also come with the constraint of mandatory conversion. Investors should carefully consider these factors before investing in MCBs.
Contingent Convertible Bonds (CoCos)
A Contingent Convertible Bond (CoCo), also known as a Contingent Capital Bond or Additional Tier 1 (AT1) capital instrument, is a hybrid debt instrument that automatically converts into equity shares under specific predefined conditions, typically when the issuing institution's capital levels fall below a certain threshold.
Key Features of CoCos:
| Feature | |
|---|---|
| Contingent Conversion: The bond automatically converts into equity shares when a specific trigger event occurs, such as a decline in the issuer's capital ratio below a predetermined level. | |
| Non-Cumulative Interest: Interest payments on CoCos may be non-cumulative, meaning that if the issuer is unable to pay interest in a particular period, it does not accrue for future payment. | |
| Write-Down or Conversion: In addition to conversion, CoCos may also be subject to a write-down, where the bond's value is reduced. | |
| Perpetual Nature: Many CoCos are perpetual, meaning they have no fixed maturity date. | |
| Higher Risk, Higher Yield: Due to their unique features and risk profile, CoCos typically offer higher yields than traditional bonds. |
How CoCos Work:
- Issuance: The financial institution issues CoCos to raise capital.
- Interest Payments: The issuer pays periodic interest payments to the bondholders.
- Trigger Event: If a predefined trigger event occurs (e.g., capital ratio falls below a certain level), the CoCos automatically convert into equity shares.
- Conversion or Write-Down: The bondholders may either have their bonds converted into equity shares or face a write-down of their investment.
Why CoCos Are Used:
- Capital Buffer: CoCos serve as a buffer to absorb losses during times of financial stress, reducing the need for government bailouts.
- Regulatory Requirement: Many regulators require financial institutions to hold a certain amount of CoCo bonds to strengthen their capital base.
- Investor Appeal: CoCos can offer attractive yields for investors willing to accept the higher risk.
Risks Associated with CoCos:
- Credit Risk: If the issuing institution fails, investors may lose their entire investment.
- Conversion Risk: Bondholders may lose their fixed-income investment and be forced to become equity shareholders.
- Write-Down Risk: The value of the bond may be reduced without conversion.
In Conclusion
CoCos are complex financial instruments that offer both opportunities and risks. While they can provide attractive yields, investors should carefully consider the potential downside and the specific terms of each CoCo before investing.
Reverse Convertible Bond (RCB)
A Reverse Convertible Bond (RCB) is a type of structured product that offers a higher-than-average coupon rate in exchange for a downside risk. At maturity, the issuer has the option to either redeem the bond for its face value or convert it into shares of an underlying asset (often a stock).
Key Features of RCBs
| Feature | |
|---|---|
| Higher Coupon Rate: RCBs typically offer higher interest rates than traditional bonds to compensate for the embedded option. | |
| Downside Risk: If the price of the underlying asset falls below a specified level (the barrier), the bondholder may receive shares of the underlying asset instead of the face value of the bond. | |
| Maturity Date: RCBs have a fixed maturity date. | |
| Barrier Level: This is the price level of the underlying asset at which the conversion option is triggered. | |
| Conversion Ratio: This determines the number of shares into which each bond can be converted. |
How RCBs Work
- Issuance: The issuer sells RCBs to investors at a par value.
- Interest Payments: The issuer pays periodic interest payments to the bondholders.
- Maturity: At maturity, the issuer has two options:
- Redemption: If the underlying asset's price is above the barrier, the issuer redeems the bond for its face value.
- Conversion: If the underlying asset's price falls below the barrier, the issuer converts the bond into shares of the underlying asset.
Risks Associated with RCBs
- Downside Risk: If the price of the underlying asset falls below the barrier, investors may lose a significant portion of their investment.
- Market Risk: The value of the RCB can fluctuate based on changes in the market price of the underlying asset.
- Credit Risk: If the issuer defaults, investors may lose their entire investment.
Why Investors Choose RCBs
- Higher Yield: RCBs offer higher interest rates than traditional bonds.
- Potential for Capital Appreciation: If the underlying asset performs well, the converted shares may appreciate in value.
In Conclusion
While RCBs can offer attractive yields, they are complex instruments with significant downside risk. Investors should carefully consider their risk tolerance and investment objectives before investing in RCBs. It's essential to understand the terms of the specific RCB, including the barrier level, conversion ratio, and the creditworthiness of the issuer.
Exchangeable Bond
An Exchangeable Bond is a type of debt security that allows the holder to exchange the bond for shares of a company other than the issuing company. This distinguishes it from a convertible bond, where the conversion is into the issuer's own shares.
Key Features of Exchangeable Bonds
| Feature | |
|---|---|
| Exchangeable for Another Company's Shares: The bondholder can exchange the bond for shares of a specified target company. | |
| Fixed Income Security: The bond pays periodic interest payments to the bondholder. | |
| Maturity Date: The bond has a fixed maturity date. | |
| Exchange Ratio: This determines the number of shares of the target company that can be exchanged for each bond. | |
| Exchange Price: The implied price per share of the target company's stock. |
How Exchangeable Bonds Work:
- Issuance: The issuing company sells exchangeable bonds to investors.
- Interest Payments: The issuer pays periodic interest payments to the bondholders.
- Exchange Option: The bondholder has the option to exchange the bond for shares of the target company at a predetermined exchange ratio.
- Maturity: At maturity, the bondholder can either exchange the bond for shares or receive the face value of the bond.
Why Companies Issue Exchangeable Bonds
- Raising Capital: Companies can raise capital without diluting their own equity.
- Strategic Investments: Exchangeable bonds can be used to acquire or invest in other companies.
- Tax Advantages: In some cases, exchangeable bonds can offer tax advantages.
Why Investors Buy Exchangeable Bonds
- Potential for Capital Appreciation: If the target company's stock price rises, the value of the exchangeable bond increases.
- Fixed Income Security: The bond provides a fixed income stream.
- Diversification: Exchangeable bonds can help investors diversify their portfolios.
Risks of Exchangeable Bonds
- Credit Risk: The risk that the issuing company may default on its debt obligations.
- Market Risk: The value of the bond can fluctuate based on changes in the market price of the target company's stock.
- Exchange Risk: The exchange ratio may not be favorable, especially if the target company's stock price declines.
In Conclusion
Exchangeable bonds offer a unique investment opportunity that combines the features of a debt security and an equity investment. However, they are complex instruments with specific risks. Investors should carefully consider their investment objectives and risk tolerance before investing in exchangeable bonds.
Real example of Convertible Bonds
Tesla's 2024 Convertible Senior Notes
Let's take a look at Tesla's 2024 Convertible Senior Notes as a real-world example. This is a great case study because it highlights the key features of convertible bonds and how they can be used to raise capital and reward investors.
Key Features of Tesla's 2024 Convertible Senior Notes:
- Face Value: $1,000 per bond
- Coupon Rate: 2% per year
- Maturity Date: March 2024
- Conversion Ratio: 3.2276 shares of common stock per $1,000 par value of the bond
- Conversion Price: $309.48 per share ($1,000 / 3.2276)
Table: Tesla's 2024 Convertible Senior Notes
| Feature | Value |
|---|---|
| Face Value | $1,000 |
| Coupon Rate | 2% |
| Maturity Date | March 2024 |
| Conversion Ratio | 3.2276 shares/bond |
| Conversion Price | $309.48/share |
How Convertible Bonds Work: Tesla Example
- Bondholder Receives Interest Payments: Until the maturity date or conversion, the bondholder receives regular interest payments (2% per year in this case).
- Conversion Option: The bondholder has the option to convert their bond into Tesla common stock at a predetermined conversion price ($309.48 per share).
- Conversion Trigger: The bondholder might choose to convert if Tesla's stock price rises above the conversion price. This allows them to participate in the potential upside of the company's growth.
Advantages of Convertible Bonds for Tesla:
- Lower Interest Rate: By offering the conversion option, Tesla can attract investors with a lower coupon rate compared to traditional bonds.
- Potential Dilution: If the bonds are converted, it will increase the number of shares outstanding, potentially diluting existing shareholders.
- Flexibility: Convertible bonds offer a hybrid structure that combines the fixed income features of bonds with the equity upside of stocks.
Advantages of Convertible Bonds for Investors:
- Fixed Income Security: Investors receive regular interest payments, providing a stable income stream.
- Equity Upside: If the stock price rises above the conversion price, investors can participate in the company's growth by converting their bonds into shares.
- Lower Risk: Compared to buying Tesla stock directly, convertible bonds offer a lower risk profile due to the fixed income component.
Note: The actual performance of Tesla's convertible bonds will depend on various factors, including the company's financial performance, market conditions, and investor sentiment.
Disclaimer: This information is for educational purposes only and does not constitute financial advice. It's important to conduct thorough research or consult with a financial advisor before making investment decisions.
Conclusion: A Diverse Landscape of Convertible Bonds
Convertible bonds offer a versatile financial instrument that blends the characteristics of both debt and equity.
Key Takeaways:
- Vanilla Convertible Bonds: These traditional bonds offer the flexibility to convert into equity shares at the bondholder's discretion.
- Mandatory Convertible Bonds: These bonds have a mandatory conversion feature, ensuring that they will convert into equity shares on a predetermined date.
- Contingent Convertible Bonds (CoCos): Designed to strengthen a financial institution's capital base, CoCos automatically convert into equity shares under specific stress conditions.
- Reverse Convertible Bonds (RCBs): These bonds offer higher-than-average coupon rates but come with downside risk, as they may convert into shares of an underlying asset if its price falls below a certain level.
- Exchangeable Bonds: These bonds allow the holder to exchange them for shares of a different company, offering exposure to a different investment opportunity.
By carefully considering the specific features, risks, and rewards of each type of convertible bond, investors can make informed decisions that align with their investment objectives and risk tolerance.