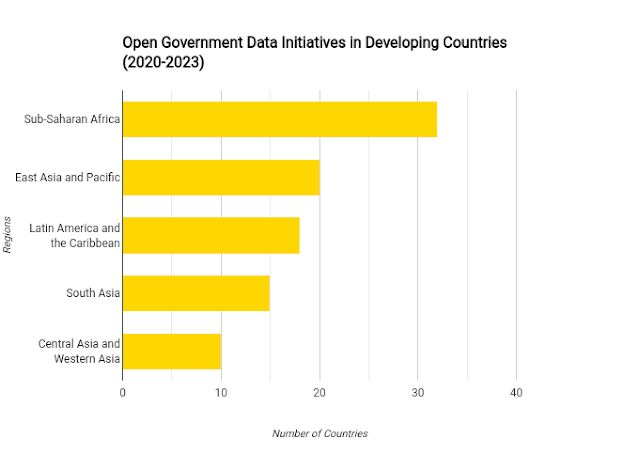
Open Government Data Initiatives in Developing Countries: A Catalyst for Transparency and Innovation
Open government data (OGD) initiatives have emerged as a powerful tool for developing countries to enhance transparency, accountability, and citizen participation. By making government data accessible to the public, these initiatives can spur innovation, improve public services, and foster economic growth.
Key Benefits of OGD Initiatives in Developing Countries
- Increased Transparency: OGD initiatives make government operations more visible to citizens, reducing corruption and promoting accountability.
- Improved Public Services: Access to government data can help identify inefficiencies and inform evidence-based policy decisions, leading to better public services.
- Economic Growth: OGD can stimulate innovation by providing entrepreneurs and researchers with valuable data to develop new products and services.
- Citizen Empowerment: By providing citizens with information, OGD can empower them to participate more meaningfully in governance and decision-making processes.
Notable OGD Initiatives in Developing Countries
| Country | Initiative Name | Key Focus |
|---|---|---|
| India | Data.gov.in | Centralized platform for government data |
| Brazil | Dados Abertos Brasil | Promoting open data culture and policies |
| Kenya | Open Data Kenya | Enhancing transparency and accountability |
| Mexico | Datos.gob.mx | Facilitating access to government information |
| Nigeria | Open Government Partnership | Promoting open government reforms |
Challenges and Opportunities
Despite the many benefits, OGD initiatives in developing countries face several challenges, including:
- Data Quality and Standardization: Ensuring data accuracy, completeness, and consistency can be a significant hurdle.
- Technical Capacity: Developing countries may lack the necessary technical infrastructure and expertise to manage and share large datasets.
- Legal and Regulatory Frameworks: Establishing clear legal frameworks for data access, reuse, and privacy is essential.
However, these challenges also present opportunities for collaboration and innovation. By working together, governments, civil society organizations, and the private sector can address these issues and harness the full potential of OGD initiatives.
Open government data initiatives are playing a vital role in driving transparency, accountability, and innovation in developing countries. By overcoming challenges and leveraging the power of data, these initiatives can contribute to sustainable development and improve the lives of citizens.
Open Government Data Initiatives in Developing Countries: India
India's National Portal for Open Government Data (Data.gov.in)
India's Data.gov.in initiative is a prime example of how open government data can be leveraged for development. Launched in 2013, the portal aims to provide a centralized platform for government data, making it accessible to citizens, researchers, and businesses.
Key Features and Impact:
- Vast Dataset: The portal hosts a diverse range of datasets, including agriculture, education, health, and infrastructure.
- API Access: Developers can access data through APIs, enabling the creation of innovative applications and services.
- Citizen Engagement: Data.gov.in has fostered citizen participation in governance and decision-making processes.
- Economic Benefits: The initiative has spurred economic growth by enabling businesses to develop new products and services based on government data.
Example Project: Agriculture Data for Farmers
One notable project utilizing Data.gov.in is the development of a mobile app to provide farmers with real-time agricultural information. The app leverages weather data, crop prices, and soil health information to help farmers make informed decisions about their crops.
Table: Impact of Data.gov.in on Agriculture
| Metric | Before Data.gov.in | After Data.gov.in |
|---|---|---|
| Crop yields | Lower | Higher |
| Farmer income | Lower | Higher |
| Access to agricultural information | Limited | Improved |
| Use of modern agricultural practices | Low | Higher |
Other Notable Projects:
- Healthcare Analytics: Analyzing healthcare data to identify disease outbreaks and improve healthcare delivery.
- Urban Planning: Using urban data to optimize transportation systems and infrastructure development.
- Education Reforms: Analyzing education data to identify disparities and improve educational outcomes.
Challenges and Lessons Learned
While Data.gov.in has achieved significant success, it has also faced challenges, including:
- Data Quality: Ensuring the accuracy and consistency of data can be a complex task.
- Technical Capacity: Building and maintaining a large-scale data platform requires technical expertise.
- Data Privacy: Protecting sensitive data while promoting openness is a delicate balance.
Lessons learned from India's experience can be applied to other developing countries seeking to implement OGD initiatives. By addressing these challenges and leveraging the potential of open data, governments can drive transparency, innovation, and sustainable development.
Open Government Data Initiatives in Brazil: A Case Study
Brazil has been a pioneer in open government data (OGD) initiatives in developing countries. Its robust commitment to transparency and accountability has led to the implementation of several successful projects.
Key OGD Initiatives in Brazil
| Initiative Name | Focus | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Dados Abertos Brasil | Centralized platform for government data | Increased transparency, improved public services, and stimulated innovation. |
| Portal da Transparência | Financial information of government agencies | Enhanced accountability and reduced corruption. |
| Portal de Dados do Governo Federal | Datasets from various government agencies | Facilitated access to information and supported research. |
Impact of OGD Initiatives in Brazil
- Increased Transparency: OGD initiatives have made government operations more visible to citizens, reducing corruption and promoting accountability.
- Improved Public Services: Access to government data has helped identify inefficiencies and inform evidence-based policy decisions, leading to better public services.
- Economic Growth: OGD has stimulated innovation by providing entrepreneurs and researchers with valuable data to develop new products and services.
- Citizen Empowerment: By providing citizens with information, OGD has empowered them to participate more meaningfully in governance and decision-making processes.
Case Study: Using OGD to Combat Deforestation
Brazil has successfully used OGD to combat deforestation in the Amazon rainforest. By making satellite imagery and deforestation data publicly available, researchers and environmental organizations have been able to track deforestation rates, identify hotspots, and support government efforts to protect the rainforest.
Challenges and Opportunities
Despite its successes, Brazil's OGD initiatives have faced challenges, including:
- Data Quality: Ensuring data accuracy, completeness, and consistency can be a significant hurdle.
- Technical Capacity: Building and maintaining a large-scale data infrastructure requires technical expertise.
- Legal and Regulatory Frameworks: Establishing clear legal frameworks for data access, reuse, and privacy is essential.
However, these challenges also present opportunities for collaboration and innovation. By working together, governments, civil society organizations, and the private sector can address these issues and harness the full potential of OGD initiatives.
Conclusion
Brazil's OGD initiatives have demonstrated the power of open data to drive transparency, accountability, and sustainable development. By overcoming challenges and leveraging the potential of OGD, Brazil has become a model for other developing countries seeking to implement similar initiatives.
Open Government Data Initiatives in Kenya
Kenya has been at the forefront of open government data (OGD) initiatives in Africa. Its commitment to transparency and accountability has led to the implementation of several successful projects.
Key OGD Initiatives in Kenya
| Initiative Name | Focus | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Open Data Kenya | Centralized platform for government data | Increased transparency, improved public services, and stimulated innovation. |
| Data Portal | Datasets from various government agencies | Facilitated access to information and supported research. |
| Open Government Partnership | Promoting open government reforms | Enhanced accountability and reduced corruption. |
Impact of OGD Initiatives in Kenya
- Increased Transparency: OGD initiatives have made government operations more visible to citizens, reducing corruption and promoting accountability.
- Improved Public Services: Access to government data has helped identify inefficiencies and inform evidence-based policy decisions, leading to better public services.
- Economic Growth: OGD has stimulated innovation by providing entrepreneurs and researchers with valuable data to develop new products and services.
- Citizen Empowerment: By providing citizens with information, OGD has empowered them to participate more meaningfully in governance and decision-making processes.
Case Study: Using OGD to Improve Healthcare
Kenya has successfully used OGD to improve healthcare delivery. By making health data publicly available, researchers and health organizations have been able to identify disease outbreaks, track immunization rates, and allocate resources more effectively.
Challenges and Opportunities
Despite its successes, Kenya's OGD initiatives have faced challenges, including:
- Data Quality: Ensuring data accuracy, completeness, and consistency can be a significant hurdle.
- Technical Capacity: Building and maintaining a large-scale data infrastructure requires technical expertise.
- Legal and Regulatory Frameworks: Establishing clear legal frameworks for data access, reuse, and privacy is essential.
However, these challenges also present opportunities for collaboration and innovation. By working together, governments, civil society organizations, and the private sector can address these issues and harness the full potential of OGD initiatives.
Conclusion
Kenya's OGD initiatives have demonstrated the power of open data to drive transparency, accountability, and sustainable development. By overcoming challenges and leveraging the potential of OGD, Kenya has become a model for other developing countries seeking to implement similar initiatives.
Open Government Data Initiatives in Mexico
Mexico has been a leader in open government data (OGD) initiatives in Latin America. Its commitment to transparency and accountability has led to the implementation of several successful projects.
Key OGD Initiatives in Mexico
| Initiative Name | Focus | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Datos.gob.mx | Centralized platform for government data | Increased transparency, improved public services, and stimulated innovation. |
| Portal de Transparencia | Financial information of government agencies | Enhanced accountability and reduced corruption. |
| Open Government Partnership | Promoting open government reforms | Facilitated access to information and supported research. |
Impact of OGD Initiatives in Mexico
- Increased Transparency: OGD initiatives have made government operations more visible to citizens, reducing corruption and promoting accountability.
- Improved Public Services: Access to government data has helped identify inefficiencies and inform evidence-based policy decisions, leading to better public services.
- Economic Growth: OGD has stimulated innovation by providing entrepreneurs and researchers with valuable data to develop new products and services.
- Citizen Empowerment: By providing citizens with information, OGD has empowered them to participate more meaningfully in governance and decision-making processes.
Case Study: Using OGD to Improve Education
Mexico has successfully used OGD to improve education outcomes. By making education data publicly available, researchers and education organizations have been able to identify disparities in access to education, track student performance, and allocate resources more effectively.
Challenges and Opportunities
Despite its successes, Mexico's OGD initiatives have faced challenges, including:
- Data Quality: Ensuring data accuracy, completeness, and consistency can be a significant hurdle.
- Technical Capacity: Building and maintaining a large-scale data infrastructure requires technical expertise.
- Legal and Regulatory Frameworks: Establishing clear legal frameworks for data access, reuse, and privacy is essential.
However, these challenges also present opportunities for collaboration and innovation. By working together, governments, civil society organizations, and the private sector can address these issues and harness the full potential of OGD initiatives.
Conclusion
Mexico's OGD initiatives have demonstrated the power of open data to drive transparency, accountability, and sustainable development. By overcoming challenges and leveraging the potential of OGD, Mexico has become a model for other developing countries seeking to implement similar initiatives.
Open Government Data Initiatives in Nigeria
Nigeria has made significant strides in open government data (OGD) initiatives, demonstrating its commitment to transparency and accountability.
Key OGD Initiatives in Nigeria
| Initiative Name | Focus | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Open Government Partnership | Promoting open government reforms | Enhanced accountability and reduced corruption. |
| Data.gov.ng | Centralized platform for government data | Increased transparency, improved public services, and stimulated innovation. |
| Open Data Initiative | Facilitating access to government information | Supported research and citizen engagement. |
Impact of OGD Initiatives in Nigeria
- Increased Transparency: OGD initiatives have made government operations more visible to citizens, reducing corruption and promoting accountability.
- Improved Public Services: Access to government data has helped identify inefficiencies and inform evidence-based policy decisions, leading to better public services.
- Economic Growth: OGD has stimulated innovation by providing entrepreneurs and researchers with valuable data to develop new products and services.
- Citizen Empowerment: By providing citizens with information, OGD has empowered them to participate more meaningfully in governance and decision-making processes.
Case Study: Using OGD to Improve Agriculture
Nigeria has successfully used OGD to improve agricultural productivity. By making agricultural data publicly available, farmers and researchers have been able to access information on weather patterns, soil conditions, and crop prices, enabling them to make informed decisions about their farming practices.
Challenges and Opportunities
Despite its successes, Nigeria's OGD initiatives have faced challenges, including:
- Data Quality: Ensuring data accuracy, completeness, and consistency can be a significant hurdle.
- Technical Capacity: Building and maintaining a large-scale data infrastructure requires technical expertise.
- Legal and Regulatory Frameworks: Establishing clear legal frameworks for data access, reuse, and privacy is essential.
However, these challenges also present opportunities for collaboration and innovation. By working together, governments, civil society organizations, and the private sector can address these issues and harness the full potential of OGD initiatives.
Conclusion
Nigeria's OGD initiatives have demonstrated the power of open data to drive transparency, accountability, and sustainable development. By overcoming challenges and leveraging the potential of OGD, Nigeria has become a model for other developing countries seeking to implement similar initiatives.
Conclusion: Open Government Data Initiatives in Developing Countries
Table: Key Takeaways from OGD Initiatives in Developing Countries
| Benefit | Impact | Challenges |
|---|---|---|
| Increased transparency | Reduces corruption, promotes accountability | Data quality, technical capacity, legal frameworks |
| Improved public services | Leads to more efficient and effective government | Data quality, technical capacity, legal frameworks |
| Economic growth | Stimulates innovation, creates new opportunities | Data quality, technical capacity, legal frameworks |
| Citizen empowerment | Enhances participation, fosters civic engagement | Data quality, technical capacity, legal frameworks |
Overall: OGD initiatives in developing countries offer significant benefits, but addressing challenges related to data quality, technical capacity, and legal frameworks is crucial for their success.
Open government data (OGD) initiatives have emerged as a powerful tool for developing countries to enhance transparency, accountability, and citizen participation. By making government data accessible to the public, these initiatives can spur innovation, improve public services, and foster economic growth.
While OGD initiatives in developing countries face several challenges, such as data quality, technical capacity, and legal frameworks, they also present significant opportunities for collaboration and innovation. By addressing these challenges and leveraging the potential of OGD, governments can drive sustainable development and improve the lives of citizens.
Key takeaways from this analysis:
- OGD initiatives can significantly improve transparency, accountability, and citizen participation in developing countries.
- OGD can lead to better public services, economic growth, and innovation.
- Challenges such as data quality, technical capacity, and legal frameworks need to be addressed to ensure the success of OGD initiatives.
- Collaboration between governments, civil society organizations, and the private sector is essential for effective OGD implementation.
By continuing to invest in OGD initiatives and addressing the associated challenges, developing countries can harness the full potential of open data to create a more transparent, accountable, and prosperous future.