Government Services in Digital Government: A Comprehensive Overview
Introduction
The advent of digital technology has revolutionized the way governments interact with their citizens. Digital government, also known as e-government, aims to deliver government services efficiently and effectively through the use of information and communication technologies (ICT). This shift has led to increased transparency, accessibility, and convenience for citizens while also improving the efficiency and effectiveness of government operations.
Key Government Services in Digital Government
Digital government offers a wide range of services to citizens, businesses, and other stakeholders. Some of the most common and essential services include:
| Service | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
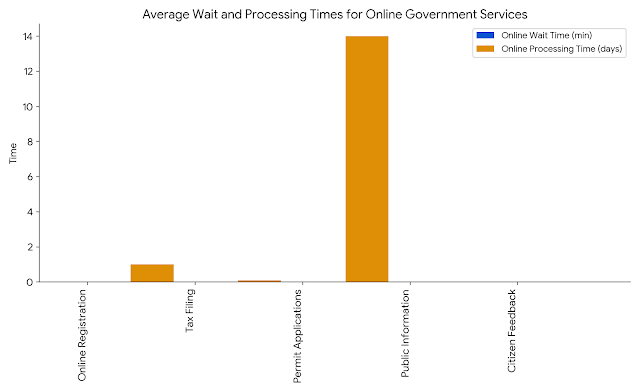
| Online Registration | Conveniently register for various government services, such as birth certificates, passports, and driver's licenses. | Online birth certificate registration |
| Tax Filing and Payment | File and pay taxes online, often with automated calculations and reminders. | E-filing income tax |
| Permit Applications | Apply for and obtain permits and licenses, such as building permits, business licenses, and environmental permits. | Online building permit application |
| Public Information | Access government information, data, and statistics. | Online public records search |
| Citizen Feedback | Provide feedback, complaints, or suggestions to government agencies. | Online complaint portal |
| E-Procurement | Conduct government procurement processes electronically, promoting transparency and efficiency. | Online tendering for government contracts |
| E-Health | Access healthcare services and information online, including electronic health records and telemedicine. | Online appointment booking with doctors |
| E-Education | Access educational resources and services online, such as online courses and distance learning programs. | Online learning platform for government employees |
| Social Services | Apply for and receive social welfare benefits and services. | Online application for unemployment benefits |
Benefits of Digital Government
Digital government offers numerous benefits to both citizens and governments, including:
- Increased Efficiency: Automation of processes reduces paperwork and speeds up service delivery.
- Improved Accessibility: Citizens can access services from anywhere at any time, reducing the need for physical visits.
- Enhanced Transparency: Online platforms provide greater transparency into government operations and decision-making.
- Reduced Costs: Digital services can be more cost-effective than traditional in-person services.
- Improved Citizen Satisfaction: Convenient and efficient services can lead to higher levels of citizen satisfaction.
Challenges and Future Trends
While digital government has many advantages, it also faces challenges, such as:
- Digital Divide: Ensuring that all citizens have access to the necessary technology and skills.
- Data Security: Protecting sensitive personal information from cyber threats.
- Interoperability: Ensuring that different government agencies can share data and systems effectively.
Despite these challenges, the future of digital government looks promising. As technology continues to evolve, we can expect to see even more innovative and efficient services being delivered to citizens.
Online Registration: A Convenient and Efficient Process
Online registration has become an integral part of our modern lives, simplifying various tasks and eliminating the need for physical visits. Whether it's registering for a course, creating an account, or applying for a service, online registration offers a convenient and efficient way to complete these tasks.
Benefits of Online Registration:
- Convenience: Accessible from anywhere with an internet connection, online registration saves time and effort.
- Efficiency: Streamlined processes and automated forms reduce paperwork and speed up the registration process.
- Accessibility: Online registration can accommodate individuals with disabilities, providing equal access to services.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Eliminating the need for physical visits can reduce overhead costs for organizations.
- Data Security: Many online registration systems employ robust security measures to protect personal information.
Common Use Cases of Online Registration:
- Education: Registering for courses, workshops, or online learning programs.
- Healthcare: Scheduling appointments, accessing medical records, or enrolling in health insurance plans.
- Government Services: Applying for permits, licenses, or government benefits.
- Events and Conferences: Registering for conferences, seminars, or social events.
- Membership Organizations: Joining clubs, associations, or professional organizations.
- Online Shopping: Creating accounts, managing orders, and subscribing to newsletters.
Key Elements of a Successful Online Registration Process:
- User-Friendly Interface: A clear and intuitive design that is easy to navigate.
- Secure Data Handling: Protection of personal information through encryption and other security measures.
- Accessibility: Compliance with accessibility standards to accommodate individuals with disabilities.
- Clear Instructions: Easy-to-understand guidance throughout the registration process.
- Efficient Validation: Verification of required fields to ensure accurate and complete information.
- Confirmation and Follow-Up: Providing confirmation messages and follow-up communication as needed.
Example of Online Registration:
A common example is registering for a new online account. This typically involves providing personal information such as name, email address, and password. Some registrations may also require additional details, such as a phone number or address. Once the information is entered, the user typically clicks a "Submit" or "Register" button to complete the process.
In conclusion, online registration has revolutionized the way we interact with organizations and services. By offering convenience, efficiency, and accessibility, it has become a valuable tool in our digital age.
Tax Filing and Payment: A Digital Revolution
Introduction
The advent of digital technology has transformed the way individuals and businesses file and pay their taxes. Tax filing and payment services, often known as e-filing or electronic tax filing, have become increasingly popular due to their convenience, efficiency, and accuracy. These services allow taxpayers to complete their tax returns and make payments online, eliminating the need for paper forms and manual processing.
Key Features of Tax Filing and Payment Services
| | Online Forms: Pre-filled forms with automated calculations and error checking. | Electronic Signature: Securely signing tax returns electronically. | Direct Deposit: Automatically depositing tax refunds directly into bank accounts. | Payment Options: Various payment methods, including credit cards, debit cards, and electronic funds transfers (EFT). | Tax Calculators: Tools to estimate tax liabilities and plan for future tax obligations. | Tax Advice: Access to tax information, resources, and advice. |
|---|
Benefits of Tax Filing and Payment Services
- Convenience: Filing and paying taxes from the comfort of home or office.
- Speed: Faster processing times compared to paper-based filing. | Accuracy: Automated calculations and error checking reduce the likelihood of mistakes. | Security: Robust security measures to protect sensitive taxpayer information. | Cost-Effectiveness: Often free or low-cost compared to traditional tax preparation services.
Common Tax Filing and Payment Services
- Government Websites: Most governments offer their own e-filing portals.
- Tax Preparation Software: Commercial software like TurboTax, H&R Block, and TaxAct.
- Professional Tax Preparers: Many tax preparers offer online filing services.
Tips for Successful Tax Filing and Payment
- Gather Necessary Documents: Collect all relevant income statements, deductions, and receipts.
- Choose the Right Service: Select a service that meets your needs and budget.
- Follow Instructions Carefully: Pay close attention to the instructions and deadlines.
- Verify Accuracy: Double-check your tax return before submitting it.
- Keep Records: Maintain copies of your tax return and supporting documents.
Future Trends in Tax Filing and Payment
As technology continues to advance, we can expect to see even more innovative tax filing and payment services. Some potential trends include:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI)-powered tax preparation: AI algorithms can analyze financial data and provide personalized tax advice.
- Blockchain-based tax records: Secure and transparent storage of tax information on a distributed ledger.
- Mobile tax apps: User-friendly apps for filing and paying taxes on smartphones and tablets.
Tax filing and payment services have revolutionized the way individuals and businesses interact with tax authorities. By offering convenience, efficiency, and accuracy, these services have made the tax filing process more accessible and less stressful. As technology continues to evolve, we can expect to see even more innovative and user-friendly solutions in the future.
Permit Applications: A Streamlined Process
Permit applications are a crucial part of many personal and business endeavors. Whether you're building a new home, starting a business, or organizing an event, obtaining the necessary permits is essential to ensure compliance with local regulations and avoid legal issues. Traditional permit application processes often involved lengthy paperwork, physical visits to government offices, and extended waiting times. However, with the advancements in technology, online permit applications have become increasingly popular, offering a more convenient and efficient way to obtain permits.
Key Features of Online Permit Applications
| | Digital Forms: Pre-filled forms with automated calculations and error checking. | Online Payments: Conveniently pay application fees using various payment methods. | Tracking Systems: Monitor the status of your application in real time. | Electronic Documents: Upload supporting documents directly to the online portal. | Notifications: Receive updates and notifications via email or SMS. | Integration with Other Services: Connect with other government services, such as zoning information or building codes. |
|---|
Benefits of Online Permit Applications
- Convenience: Apply for permits from the comfort of your home or office.
- Efficiency: Reduce paperwork and expedite the application process. | Transparency: Access real-time information about the status of your application. | Cost-Effectiveness: Potentially lower fees or eliminate the need for physical visits. | Accessibility: Accommodate individuals with disabilities by providing online access.
Common Permit Applications
- Building Permits: For construction projects, renovations, or additions.
- Business Licenses: To operate a business within a specific jurisdiction. | Event Permits: For organizing events, such as festivals, concerts, or parades. | Zoning Permits: To ensure land use complies with local zoning regulations. | Environmental Permits: For activities that may impact the environment, such as pollution control or waste management.
Tips for Successful Permit Applications
- Research Requirements: Understand the specific requirements for the permit you need. | Gather Necessary Documents: Prepare all supporting documents, such as property deeds, blueprints, and financial information. | Complete Forms Accurately: Ensure that all information is correct and complete. | Follow Instructions Carefully: Adhere to any specific guidelines or deadlines. | Monitor the Process: Track the progress of your application and address any questions or concerns promptly.
Future Trends in Permit Applications
As technology continues to advance, we can expect to see even more innovative and user-friendly permit application services. Some potential trends include:
- Integration with Geographic Information Systems (GIS): Visualize permit locations and zoning information on maps. | Artificial Intelligence (AI)-powered assistance: AI can help guide applicants through the process and provide personalized advice. | Mobile apps for permit applications: Conveniently apply for permits on smartphones and tablets.
Online permit applications have significantly streamlined the process of obtaining permits, making it more convenient and efficient for individuals and businesses. By leveraging technology, these services have reduced paperwork, expedited processing times, and improved transparency. As technology continues to evolve, we can expect to see even more innovative solutions that further simplify the permit application process.
Public Information: Accessing Government Data and Resources
Public information refers to the availability of government data, statistics, and other resources to the public. This information is essential for citizens, researchers, journalists, and businesses to make informed decisions and hold governments accountable. In recent years, there has been a significant push towards open government initiatives, which aim to increase transparency and access to public information.
Key Features of Public Information Services
| | Data Portal: A centralized platform for accessing government datasets in various formats. | Search Functionality: Robust search capabilities to locate specific information. | Metadata: Detailed descriptions of datasets, including data sources, definitions, and updates. | Visualization Tools: Interactive tools to visualize data and trends. | APIs: Application programming interfaces (APIs) for developers to access and integrate data into their applications. | Citizen Engagement: Opportunities for public input and feedback on data and information. |
|---|
Benefits of Public Information Services
- Transparency: Increased transparency into government operations and decision-making. | Accountability: Holds governments accountable by providing access to information. | Informed Decision-Making: Enables citizens, businesses, and researchers to make informed choices. | Innovation: Fosters innovation by providing data for research and development. | Economic Development: Supports economic growth by providing valuable information to businesses.
Common Types of Public Information
- Government Budgets and Expenditures: Information on how government funds are allocated and spent. | Economic Data: Statistics on GDP, employment, inflation, and other economic indicators. | Health Data: Information on disease prevalence, healthcare utilization, and public health initiatives. | Education Data: Statistics on student enrollment, academic performance, and educational outcomes. | Environmental Data: Data on air quality, water quality, and climate change. | Crime Data: Statistics on crime rates, types of crimes, and law enforcement activities.
Challenges and Future Trends
While public information services offer numerous benefits, they also face challenges, such as:
- Data Quality: Ensuring the accuracy, completeness, and reliability of data. | Data Privacy: Protecting sensitive personal information while making data publicly available. | Technical Barriers: Providing access to data in a user-friendly and accessible format. | Digital Divide: Addressing the gap in access to technology and information among different populations.
Despite these challenges, the future of public information looks promising. As technology continues to advance, we can expect to see even more innovative and accessible public information services. Some potential trends include:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI)-powered data analysis: AI can help analyze large datasets and identify trends and patterns. | Open Data Standards: Adoption of standardized data formats and metadata to improve interoperability. | Citizen Science: Engaging citizens in data collection and analysis to enhance the quality and quantity of public information.
Public information services play a vital role in promoting transparency, accountability, and informed decision-making. By providing access to government data and resources, these services empower citizens, businesses, and researchers to understand and participate in the democratic process. As technology continues to evolve, we can expect to see even more innovative and accessible public information services that benefit society as a whole.
Citizen Feedback: A Vital Tool for Government Improvement
Citizen feedback is essential for governments to understand the needs, concerns, and satisfaction levels of their constituents. By actively seeking and responding to feedback, governments can improve their services, policies, and overall performance. Citizen feedback can come in various forms, such as surveys, online portals, public meetings, and social media.
Key Features of Citizen Feedback Services
| | Online Portals: User-friendly platforms for submitting feedback and suggestions. | Surveys: Structured questionnaires to gather specific information from citizens. | Social Media Monitoring: Tracking public sentiment and feedback on social media platforms. | Public Meetings: Opportunities for direct interaction between citizens and government officials. | Feedback Analysis: Tools to analyze feedback data and identify trends and patterns. | Response Tracking: Systems to track the status of feedback and ensure timely responses. |
|---|
Benefits of Citizen Feedback Services
- Improved Governance: Helps governments identify and address issues that are important to citizens. | Increased Transparency: Demonstrates a commitment to transparency and accountability. | Enhanced Citizen Satisfaction: Boosts citizen satisfaction by addressing their needs and concerns. | Informed Decision-Making: Provides valuable insights for policymakers and government officials. | Innovation: Fosters innovation by encouraging citizens to share their ideas and suggestions.
Common Topics for Citizen Feedback
- Public Services: Quality of services such as education, healthcare, and transportation. | Infrastructure: Condition of roads, bridges, and public facilities. | Economic Development: Job creation, economic growth, and business climate. | Environmental Issues: Sustainability, pollution control, and natural resource management. | Social Issues: Affordable housing, poverty reduction, and social justice.
Tips for Effective Citizen Feedback
- Encourage Participation: Make it easy for citizens to provide feedback through multiple channels. | Respond Timely: Acknowledge feedback promptly and provide updates on progress. | Analyze Data: Use data analysis tools to identify trends and prioritize issues. | Incorporate Feedback: Implement changes based on citizen feedback and communicate the results. | Measure Impact: Evaluate the effectiveness of citizen feedback initiatives.
Future Trends in Citizen Feedback
As technology continues to evolve, we can expect to see even more innovative and effective citizen feedback services. Some potential trends include:
- AI-powered feedback analysis: AI can help analyze large volumes of feedback data and identify key themes and patterns. | Mobile apps for feedback: Conveniently submit feedback on smartphones and tablets. | Gamification of feedback: Using game-based elements to make feedback collection more engaging. | Social media integration: Deeper integration with social media platforms to capture a wider range of feedback.
Citizen feedback is a valuable tool for governments to improve their performance and better serve their constituents. By actively seeking and responding to feedback, governments can build trust, enhance transparency, and create a more responsive and effective public sector. As technology continues to advance, we can expect to see even more innovative and effective citizen feedback services that help governments connect with their citizens and address their needs.
E-Procurement: Streamlining Government Procurement
E-procurement, or electronic procurement, is the use of information and communication technology (ICT) to manage the entire procurement process, from planning to contract execution. It involves the electronic exchange of information and documents between buyers and sellers, streamlining the procurement cycle and improving efficiency, transparency, and accountability.
Key Features of E-Procurement Systems
| Online Catalogs: Centralized repositories of products and services from various suppliers. | Request for Proposals (RFPs): Electronic publishing and management of RFPs. | Bid Submission: Online submission of bids and proposals. | Reverse Auctions: Online auctions where buyers set the price and suppliers compete to provide the best terms. | Contract Management: Electronic contract creation, execution, and management. | Supplier Performance Management: Tracking and evaluating supplier performance.
Benefits of E-Procurement
- Efficiency: Streamlines procurement processes, reducing time and costs. | Transparency: Increases transparency by providing public access to procurement information. | Accountability: Improves accountability by tracking and monitoring procurement activities. | Cost Reduction: Reduces procurement costs through competitive bidding and negotiation. | Improved Supplier Relationships: Fosters stronger relationships with suppliers through electronic communication and collaboration.
Common E-Procurement Applications
- Goods and Services: Procurement of office supplies, equipment, and services. | Construction Contracts: Procurement of construction projects. | IT Services: Procurement of information technology services and hardware. | Public Works: Procurement of public infrastructure projects.
Challenges and Best Practices
- Security: Protecting sensitive data and ensuring the integrity of the procurement process. | Integration: Integrating e-procurement systems with other government systems and databases. | User Adoption: Encouraging user adoption and training among procurement professionals. | Data Quality: Ensuring the accuracy and completeness of data used in the procurement process. | Supplier Diversity: Promoting supplier diversity and inclusion in procurement processes.
Future Trends in E-Procurement
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): Leveraging AI to automate tasks, analyze data, and optimize procurement processes. | Blockchain Technology: Using blockchain to ensure the security and transparency of procurement transactions. | Internet of Things (IoT): Integrating IoT devices to track inventory, monitor assets, and optimize procurement decisions. | Cloud-Based E-Procurement: Deploying e-procurement solutions in the cloud for scalability and flexibility.
E-procurement has become an essential tool for governments to streamline their procurement processes, improve efficiency, and enhance transparency. By leveraging technology, governments can reduce costs, improve accountability, and foster stronger relationships with suppliers. As technology continues to evolve, we can expect to see even more innovative and effective e-procurement solutions that benefit both governments and taxpayers.
E-Health: Transforming Healthcare Delivery
E-health, or electronic health, refers to the use of information and communication technology (ICT) to improve healthcare delivery. It encompasses a wide range of applications, including electronic health records (EHRs), telemedicine, mobile health (mHealth), and health information systems. E-health has the potential to revolutionize healthcare by enhancing access, improving efficiency, and improving patient outcomes.
Key Features of E-Health Services
| | Electronic Health Records (EHRs): Digital records of patient health information, including medical history, medications, allergies, and test results. | Telemedicine: Remote delivery of healthcare services, such as consultations and diagnoses, using telecommunications technology. | Mobile Health (mHealth): Using mobile devices, such as smartphones and tablets, to deliver healthcare services and information. | Health Information Systems: Integrated systems for managing healthcare data and processes. | Health Information Exchanges (HIEs): Networks that allow healthcare providers to share patient information electronically. |
|---|
Benefits of E-Health Services
- Improved Access: Increases access to healthcare services, especially in rural or underserved areas. | Enhanced Efficiency: Streamlines administrative tasks and improves the efficiency of healthcare delivery. | Improved Quality of Care: Ensures better coordination of care, reduces medical errors, and improves patient outcomes. | Patient Empowerment: Empowers patients to take a more active role in their own healthcare. | Cost Reduction: Reduces healthcare costs by improving efficiency and reducing waste.
Common E-Health Applications
- Patient Portals: Online portals that allow patients to access their medical records, schedule appointments, and communicate with healthcare providers. | Remote Monitoring: Using wearable devices and sensors to monitor patients' health conditions remotely. | Telemedicine Consultations: Conducting virtual consultations between patients and healthcare providers. | Electronic Prescribing (ePrescribing): Prescribing medications electronically to reduce errors and improve safety. | Health Information Exchanges: Sharing patient information among healthcare providers to improve coordination of care.
Challenges and Future Trends
- Data Privacy and Security: Protecting sensitive patient data from unauthorized access. | Interoperability: Ensuring that different healthcare systems can communicate and exchange information seamlessly. | Digital Divide: Addressing the gap in access to technology and information among different populations. | Regulatory Challenges: Navigating complex regulatory frameworks and ensuring compliance.
Despite these challenges, the future of e-health looks promising. As technology continues to advance, we can expect to see even more innovative and effective e-health solutions. Some potential trends include:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): Using AI to analyze medical data, diagnose diseases, and personalize treatment plans. | Internet of Things (IoT): Integrating IoT devices to monitor patient health and improve care delivery. | Blockchain Technology: Using blockchain to secure and share patient data securely. | Virtual Reality (VR): Using VR for medical training, patient education, and therapy.
E-health has the potential to transform healthcare delivery by improving access, enhancing efficiency, and improving patient outcomes. By leveraging technology, healthcare providers can deliver better care, reduce costs, and empower patients to take a more active role in their own health. As technology continues to evolve, we can expect to see even more innovative and effective e-health solutions that benefit patients, healthcare providers, and society as a whole.
E-Education: Learning Beyond the Classroom
E-education, or electronic education, refers to the use of information and communication technology (ICT) to deliver educational services. It encompasses a wide range of applications, including online courses, distance learning, virtual classrooms, and educational software. E-education has the potential to revolutionize education by providing flexible, accessible, and personalized learning experiences.
Key Features of E-Education Services
| | Online Courses: Self-paced courses that can be accessed anytime, anywhere. | Distance Learning: Programs that allow students to learn from a distance, often combining online and offline components. | Virtual Classrooms: Interactive online environments where students and teachers can collaborate and communicate in real-time. | Educational Software: Computer-based tools and applications that enhance learning. | Learning Management Systems (LMS): Platforms for managing and delivering educational content. |
|---|
Benefits of E-Education Services
- Flexibility: Allows students to learn at their own pace and on their own schedule. | Accessibility: Provides access to education for individuals in remote or underserved areas. | Personalized Learning: Tailors learning experiences to individual needs and preferences. | Cost-Effectiveness: Can be more cost-effective than traditional face-to-face instruction. | Global Reach: Connects learners from around the world, fostering cultural exchange and understanding.
Common E-Education Applications
- K-12 Education: Online courses and supplemental materials for K-12 students. | Higher Education: Online degree programs, certificate courses, and continuing education. | Corporate Training: Online training programs for employees and professionals. | Language Learning: Online language courses and language learning apps. | Professional Development: Continuing education for professionals in various fields.
Challenges and Future Trends
- Quality Assurance: Ensuring the quality and effectiveness of online courses. | Equity and Access: Addressing the digital divide and ensuring equal access to e-education. | Social Interaction: Promoting social interaction and collaboration among online learners. | Teacher Training: Providing adequate training and support for teachers to effectively use e-education tools.
Despite these challenges, the future of e-education looks promising. As technology continues to advance, we can expect to see even more innovative and effective e-education solutions. Some potential trends include:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): Using AI to personalize learning experiences and provide intelligent tutoring. | Virtual Reality (VR): Using VR for immersive and interactive learning experiences. | Gamification: Incorporating game-based elements to make learning more engaging. | Blockchain Technology: Using blockchain to ensure the security and authenticity of educational credentials.
E-education has the potential to transform education by providing flexible, accessible, and personalized learning experiences. By leveraging technology, educators can create engaging and effective learning environments that cater to the needs of diverse learners. As technology continues to evolve, we can expect to see even more innovative and effective e-education solutions that benefit students, educators, and society as a whole.
Social Services: Supporting Individuals and Communities
Social services are essential for supporting individuals and communities, especially those facing challenges such as poverty, disability, illness, or social isolation. Social service agencies provide a wide range of programs and services to help people meet their basic needs, improve their quality of life, and build stronger communities.
Key Features of Social Services
| | Needs Assessment: Identifying the specific needs of individuals and communities. | Case Management: Providing individualized support and guidance to clients. | Counseling and Therapy: Offering counseling and therapy services to address mental health and emotional well-being. | Support Groups: Facilitating support groups for individuals facing similar challenges. | Community Outreach: Reaching out to vulnerable populations and providing resources and information. | Advocacy: Advocating for policies and programs that support the needs of vulnerable populations. |
|---|
Common Types of Social Services
- Income Assistance: Providing financial assistance to individuals and families in need. | Housing Assistance: Helping individuals and families find affordable housing. | Healthcare Services: Assisting individuals in accessing healthcare services. | Child Welfare Services: Protecting children and providing support to families. | Disability Services: Providing support and services to individuals with disabilities. | Substance Abuse Treatment: Offering treatment programs for individuals struggling with substance abuse.
Benefits of Social Services
- Improved Quality of Life: Helping individuals and families overcome challenges and improve their living conditions. | Community Strengthening: Building stronger and more resilient communities. | Social Justice: Promoting social justice and equity by addressing inequality and discrimination. | Economic Development: Contributing to economic development by supporting vulnerable populations and reducing poverty.
Challenges and Future Trends
- Funding Shortages: Ensuring adequate funding for social service programs. | Staffing Shortages: Recruiting and retaining qualified staff. | Changing Needs: Adapting to the changing needs of individuals and communities. | Integration of Services: Coordinating and integrating social services to provide more comprehensive support.
Despite these challenges, the future of social services looks promising. As technology continues to evolve, we can expect to see even more innovative and effective social service programs. Some potential trends include:
- Technology-Enabled Services: Using technology to deliver social services more efficiently and effectively. | Community-Based Initiatives: Empowering communities to take a more active role in providing social services. | Partnerships with the Private Sector: Collaborating with businesses and organizations to address social needs. | Data-Driven Decision-Making: Using data to inform social service policies and programs.
Social services are essential for supporting individuals and communities, especially those facing challenges. By providing a wide range of programs and services, social service agencies can help people meet their basic needs, improve their quality of life, and build stronger communities. As technology continues to evolve, we can expect to see even more innovative and effective social service programs that benefit individuals and society as a whole.