Androgenic Alopecia Treatment for Women with PCOS
Understanding Androgenic Alopecia and PCOS
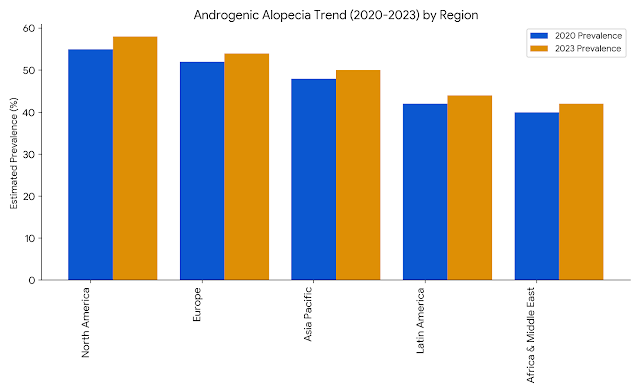
Androgenic alopecia, also known as male-pattern baldness, is a common hair loss condition that can affect both men and women. In women, it often manifests as thinning hair on the top of the head and along the hairline. Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a hormonal disorder that can contribute to androgenic alopecia in women.
Treatment Options
There are several treatment options available for women with PCOS who are experiencing androgenic alopecia. The most effective approach often involves a combination of treatments tailored to individual needs.
| Treatment Option | Description | Effectiveness |
|---|---|---|
| Minoxidil | A topical medication that stimulates hair growth. It is often effective for women with mild to moderate hair loss. | Moderate to high |
| Hormonal Therapy | Medications like birth control pills or anti-androgen drugs can help regulate hormone levels and reduce hair loss. | Moderate to high |
| Low-Androgen Diet | A diet low in foods that can increase androgen levels, such as red meat, dairy, and processed foods, can be beneficial. | Moderate |
| Lifestyle Changes | Reducing stress, getting enough sleep, and avoiding harsh hair treatments can help promote hair health. | Low to moderate |
| Hair Restoration Procedures | Options like hair transplantation or laser hair therapy can be considered for more severe cases of hair loss. | High, but expensive |
Choosing the Right Treatment
The best treatment for androgenic alopecia in women with PCOS will depend on several factors, including the severity of hair loss, overall health, and personal preferences. It's important to consult with a healthcare professional to discuss the options and determine the most appropriate course of action.
Additional Considerations
- Patience is Key: Hair growth can take time, and it may be several months before noticeable results are seen.
- Combination Therapy: Combining multiple treatments often yields better results than using a single approach.
- Ongoing Management: Androgenic alopecia is a chronic condition, and ongoing treatment may be necessary to maintain hair growth.
By understanding the causes and available treatments for androgenic alopecia in women with PCOS, individuals can take proactive steps to manage their hair loss and improve their quality of life.
Minoxidil: A Treatment for Hair Loss
What is Minoxidil?
Minoxidil is a topical medication that is used to treat hair loss in men and women. It works by stimulating hair follicles to grow new hair and thicken existing hair.
How Does Minoxidil Work?
The exact mechanism by which minoxidil works is not fully understood, but it is believed to:
- Dilate blood vessels: This increases blood flow to the scalp, which may help to nourish hair follicles.
- Stimulate hair growth: Minoxidil may directly stimulate hair follicles to enter the growth phase of their life cycle.
Effectiveness of Minoxidil
The effectiveness of minoxidil varies from person to person. However, studies have shown that it can be effective in:
- Treating male-pattern baldness: Minoxidil can help to slow down hair loss and promote new hair growth in men with androgenic alopecia.
- Treating female-pattern baldness: Minoxidil can also be effective in treating hair loss in women, particularly when it occurs on the top of the head.
How to Use Minoxidil
Minoxidil is typically applied to the scalp twice a day, once in the morning and once at night. It is important to follow the instructions on the label carefully.
Side Effects of Minoxidil
Minoxidil can cause some side effects, including:
- Scalp irritation: Some people may experience redness, itching, or flaking of the scalp.
- Rapid heartbeat: In rare cases, minoxidil can cause a rapid heartbeat.
- Unintended hair growth: Minoxidil can sometimes cause hair to grow in unwanted places, such as the face or chest.
Table: Minoxidil Usage and Side Effects
| Benefit | Potential Side Effects |
|---|---|
| Stimulates hair growth | Scalp irritation, rapid heartbeat, unintended hair growth |
| Treats male-pattern baldness | Can be expensive |
| Treats female-pattern baldness | May take several months to see results |
| Easy to use | Can be messy |
Important Considerations
- Consistency is key: It is important to use minoxidil consistently for several months to see results.
- Consult a doctor: If you are considering using minoxidil, it is important to talk to your doctor to discuss the risks and benefits.
- Not a cure-all: Minoxidil is not a cure for hair loss. It can help to slow down hair loss and promote new hair growth, but it may not be effective for everyone.
If you have any concerns about using minoxidil, please consult with a healthcare professional.
Hormonal Therapy for Androgenic Alopecia in Women with PCOS
Understanding Hormonal Therapy
Hormonal therapy is a treatment approach that involves using medications to regulate hormone levels. In women with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) who are experiencing androgenic alopecia, hormonal therapy can be an effective way to address both conditions.
Types of Hormonal Therapy
There are several types of hormonal therapy that may be used to treat androgenic alopecia in women with PCOS:
| Treatment Type | Medications | How it Works |
|---|---|---|
| Combined Oral Contraceptives (COCs) | Birth control pills containing estrogen and progestin | Reduces androgen production, regulates menstrual cycles, and can improve hair growth. |
| Anti-androgens | Spironolactone, flutamide | Directly blocks the action of androgens, which can reduce hair loss and improve hair growth. |
| Progestins | Cyproterone acetate | Reduces androgen production and can improve hair growth. |
| Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone (GnRH) Agonists | Leuprolide acetate, goserelin acetate | Suppresses the production of both estrogen and androgen, which can be effective for severe cases of hair loss. |
Benefits of Hormonal Therapy
- Reduces hair loss: Hormonal therapy can help to slow down or stop hair loss caused by excessive androgen production.
- Improves hair growth: In some cases, hormonal therapy can stimulate new hair growth.
- Addresses other symptoms of PCOS: Hormonal therapy can also help to manage other symptoms of PCOS, such as irregular menstrual cycles, acne, and infertility.
Potential Side Effects
Hormonal therapy may cause some side effects, including:
- Headaches
- Breast tenderness
- Weight gain
- Mood changes
- Increased risk of blood clots
Choosing the Right Hormonal Therapy
The best type of hormonal therapy for a woman with PCOS and androgenic alopecia will depend on several factors, such as the severity of hair loss, other symptoms of PCOS, and individual preferences. It is important to discuss the options with a healthcare provider to determine the most appropriate course of action.
Important Considerations
- Long-term use: Hormonal therapy may need to be used long-term to maintain hair growth and manage other symptoms of PCOS.
- Regular monitoring: Regular follow-up with a healthcare provider is important to monitor the effectiveness of the treatment and address any side effects.
- Individual response: The response to hormonal therapy can vary from person to person.
If you are considering hormonal therapy for androgenic alopecia or PCOS, please consult with a healthcare professional to discuss the risks and benefits.
Low-Androgen Diet for Women with PCOS and Androgenic Alopecia
Understanding the Link Between Androgens and Hair Loss
Androgens are male sex hormones that are also present in women, albeit in smaller amounts. When androgen levels are elevated, it can lead to hair loss, a condition known as androgenic alopecia. Women with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) often have higher-than-normal androgen levels, which can contribute to hair loss.
The Role of Diet
While there is no definitive scientific evidence that diet can directly cause or cure androgenic alopecia, some studies suggest that a low-androgen diet may be beneficial for women with PCOS. By reducing the intake of foods that can stimulate androgen production, women may be able to improve their hair health and reduce hair loss.
Foods to Limit or Avoid
| Food Category | Examples | Reason to Limit |
|---|---|---|
| Refined carbohydrates | White bread, pasta, white rice | Can increase insulin levels, which may stimulate androgen production. |
| Processed foods | Fast food, packaged snacks | Often high in refined carbohydrates, unhealthy fats, and added sugars. |
| Red meat | Beef, pork, lamb | Can increase androgen levels. |
| Dairy products | Milk, cheese, yogurt | May contain hormones that can stimulate androgen production. |
| Soy products | Tofu, tempeh, soy milk | While soy is generally considered healthy, excessive consumption can increase estrogen levels, which may indirectly affect androgen production. |
Foods to Incorporate
| Food Category | Examples | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Fruits and vegetables | Berries, leafy greens, citrus fruits | Rich in antioxidants and vitamins, which can promote hair health. |
| Whole grains | Brown rice, quinoa, whole-wheat bread | Provide fiber and complex carbohydrates, which can help regulate blood sugar levels. |
| Lean proteins | Fish, poultry, beans | Provide essential nutrients for hair growth without increasing androgen levels. |
| Healthy fats | Avocado, nuts, seeds | Can help to balance hormones and promote overall health. |
Additional Tips
- Moderate alcohol consumption: Excessive alcohol intake can disrupt hormone balance and contribute to hair loss.
- Manage stress: Chronic stress can exacerbate hair loss. Practice stress-management techniques like meditation or yoga.
- Consult a healthcare professional: Before making significant changes to your diet, it's important to consult with a healthcare provider or registered dietitian.
Remember: While a low-androgen diet may be beneficial for some women with PCOS and androgenic alopecia, individual results may vary. It's important to combine dietary changes with other treatment options, such as hormonal therapy or medications, to achieve optimal results.
Lifestyle Changes for Androgenic Alopecia in Women with PCOS
Understanding the Impact of Lifestyle on Hair Health
While genetics and hormonal factors play a significant role in androgenic alopecia, certain lifestyle factors can also contribute to hair loss or hinder hair growth. By making positive changes to your lifestyle, you can support overall hair health and potentially improve the appearance of your hair.
Key Lifestyle Changes
| Lifestyle Change | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Stress Management | Excessive stress can trigger hair loss. Practicing stress-reduction techniques like meditation, yoga, or deep breathing can help. |
| Adequate Sleep | Lack of sleep can disrupt hormone balance and impair hair growth. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night. |
| Balanced Diet | A healthy, balanced diet provides essential nutrients for hair growth, such as iron, zinc, biotin, and protein. |
| Regular Exercise | Physical activity can improve blood circulation to the scalp, promoting hair growth. |
| Gentle Hair Care | Avoid harsh hair treatments like excessive heat styling, tight hairstyles, and chemical treatments that can damage hair. |
| Scalp Care | Keep your scalp clean and healthy by using gentle shampoos and avoiding excessive scratching or scrubbing. |
| Limit Alcohol and Tobacco | Excessive alcohol consumption and smoking can negatively impact hair health. |
Additional Tips
- Consider scalp massages: Regular scalp massages can stimulate blood flow and promote hair growth.
- Protect your hair from the sun: Exposure to excessive sunlight can damage hair. Wear a hat or use a hair product with UV protection.
- Be patient: Hair growth takes time. It may take several months to see noticeable results from lifestyle changes.
Remember: While lifestyle changes can be helpful, they may not be sufficient for everyone. If you're experiencing significant hair loss, it's important to consult with a healthcare professional to discuss other treatment options, such as hormonal therapy or medications.
Hair Restoration Procedures for Women with PCOS and Androgenic Alopecia
Overview
For women with PCOS and androgenic alopecia who have experienced significant hair loss, hair restoration procedures may be considered. These procedures can help to restore hair density and improve overall hair appearance.
Common Hair Restoration Procedures
| Procedure | Description | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hair Transplantation | Surgically transplanting hair follicles from a donor area (usually the back of the head) to the affected area. | Natural-looking results, permanent. | Invasive, expensive, may require multiple procedures. |
| Scalp Micropigmentation | A non-surgical procedure that involves tattooing tiny dots of pigment onto the scalp to mimic the appearance of shaved hair. | Quick, relatively inexpensive, can be combined with other treatments. | May not be as natural-looking as hair transplantation, may fade over time. |
| Laser Hair Therapy | Using low-level lasers to stimulate hair follicles and promote hair growth. | Non-invasive, minimal downtime, can be combined with other treatments. | May require multiple sessions, results may vary. |
| Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy | Injecting concentrated platelets from your own blood into the scalp to stimulate hair growth. | Non-invasive, uses your own blood, may improve hair quality. | Expensive, may require multiple sessions, results may vary. |
Choosing the Right Procedure
The most suitable hair restoration procedure will depend on several factors, including:
- Severity of hair loss: More advanced cases of hair loss may require more extensive procedures.
- Desired outcome: Consider your goals for hair restoration, such as density, coverage, and natural appearance.
- Budget: Hair restoration procedures can be expensive.
- Individual factors: Your overall health, hair type, and response to treatments will influence the choice of procedure.
Important Considerations
- Consult a specialist: It's crucial to consult with a qualified hair restoration surgeon or dermatologist to discuss your options and determine the best approach for your specific needs.
- Realistic expectations: Hair restoration procedures may not completely restore your hair to its pre-hair loss state. It's important to have realistic expectations about the potential results.
- Combination therapies: In some cases, combining hair restoration procedures with other treatments, such as hormonal therapy or medications, may yield better results.If you have any questions or concerns about hair restoration procedures, please consult with a healthcare professional.
Conclusion: Androgenic Alopecia Treatment for Women with PCOS
Androgenic alopecia is a common hair loss condition that can significantly impact the quality of life for women with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). While there is no cure for this condition, various treatment options can help manage hair loss and promote hair growth.
Key Treatment Approaches
- Hormonal therapy: Medications like birth control pills, anti-androgens, and progestins can help regulate hormone levels and reduce hair loss.
- Minoxidil: A topical medication that stimulates hair growth.
- Low-androgen diet: Reducing the intake of foods that can increase androgen levels may be beneficial.
- Lifestyle changes: Managing stress, getting enough sleep, and avoiding harsh hair treatments can support hair health.
- Hair restoration procedures: For more severe cases of hair loss, procedures like hair transplantation or laser hair therapy may be considered.
Choosing the Right Treatment
The best treatment approach will depend on individual factors, including the severity of hair loss, overall health, and personal preferences. It's essential to consult with a healthcare professional to discuss the options and develop a personalized treatment plan.
Ongoing Management
Androgenic alopecia is a chronic condition, and ongoing management may be necessary to maintain hair growth and address any associated symptoms. Regular follow-up with a healthcare provider is important to monitor progress and adjust treatment as needed.
By understanding the causes and available treatments for androgenic alopecia in women with PCOS, individuals can take proactive steps to manage their hair loss and improve their quality of life.