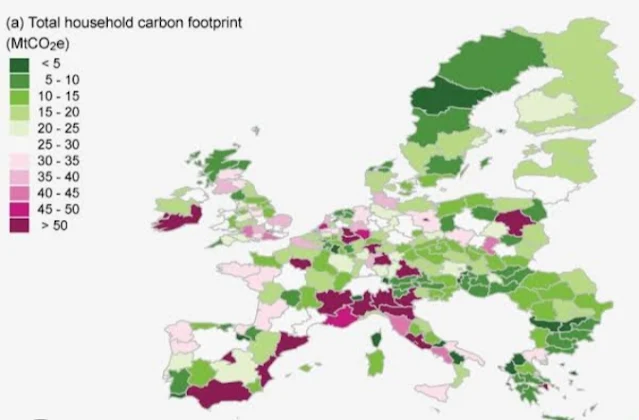
The Rising Tide of Carbon: A Regional Look at Our Growing Footprint
The shadow of our carbon footprint looms large, stretching across the globe and leaving an undeniable mark on the planet.
While the overall trend points towards an alarming rise in emissions, a closer look reveals a complex tapestry woven with regional variations, contrasting narratives, and glimmers of hope.
The Rising Tide of Carbon
| Year | Atmospheric CO2 Concentration (ppm) | Global Average Temperature (°C) |
|---|---|---|
| 1958 | 315 | 14.5 |
| 1970 | 325 | 14.6 |
| 1980 | 338 | 14.8 |
| 1990 | 353 | 15.0 |
| 2000 | 367 | 15.2 |
| 2010 | 389 | 15.5 |
| 2020 | 417 | 15.8 |
| 2030 (projected) | 440 | 16.1 |
Note: These data are based on estimates from the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC). Actual values may vary slightly.
Source: National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) and IPCC
Developed Nations: Declining Emissions, Uneven Progress
In regions like Europe and North America, once the world's biggest emitters, a downward trend in carbon footprint is taking hold. Stringent regulations, investments in renewable energy, and increased public awareness have contributed to this positive shift. The UK, for instance, has managed to halve its emissions since 1970, demonstrating the potential for significant reductions. However, this progress is not uniform. Certain sectors, like transportation, continue to lag behind, and concerns remain about "offshoring" emissions by importing goods produced elsewhere with less stringent environmental standards.
Developing Nations: Growth and Growing Emissions
The picture in developing nations is considerably different. Here, rapid economic growth often translates to rising emissions. As populations move toward higher living standards, their demand for energy and resource-intensive products increases. China, now the world's largest emitter, exemplifies this trend. While some progress in clean energy investments and efficiency measures is evident, it's outpaced by the sheer scale of development. However, it's crucial to acknowledge that developed nations bear a historical responsibility for a significant portion of the accumulated carbon in the atmosphere, and supporting sustainable development pathways in emerging economies is critical for tackling the climate crisis collectively.
Regional Nuances and Emerging Trends
Beyond these broad narratives, regional specificities paint a more nuanced picture. For instance, Latin America boasts vast potential for renewable energy sources like solar and wind, offering a chance to decouple economic growth from emissions. Similarly, Southeast Asia is witnessing a rise in green infrastructure investments, showcasing its commitment to a sustainable future.
Individual Choices and Systemic Change: A Shared Responsibility
While regional trends paint a complex picture, one thing remains clear: addressing the challenge of climate change demands a multi-pronged approach. Individual choices, from opting for sustainable transportation to reducing energy consumption, have a cumulative impact. However, systemic changes like carbon pricing, stricter regulations, and investments in clean technologies are equally crucial.
The rising tide of carbon emissions may seem daunting, but it's not an inevitable fate. By acknowledging the regional variations, understanding the challenges and opportunities, and embracing a spirit of collective responsibility, we can turn the tide and chart a course towards a more sustainable future for all.
Carbon Footprint By Region: Statistics Data
Carbon Footprint by Region: Statistics & Data Roundup
Understanding the regional distribution of carbon footprint is crucial for effective climate action strategies. Here's a compilation of key statistics and data sources:
Global Overview:
- Total global CO2 emissions in 2022: 36.1 GtCO2 (gigatonnes of carbon dioxide) (Source: IEA)
- Projected change in 2023: Slight increase (Source: IEA)
- Largest emitters: China (27%), North America (24%), and Europe (10%) (Source: Our World in Data)
Developed vs. Developing Nations:
- Developed nations:
- Generally decreasing emissions but with variations.
- Example: UK emissions halved since 1970 (Source: Our World in Data)
- Challenges: "offshoring" emissions through imports.
- Developing nations:
- Rising emissions due to rapid economic growth.
- Example: China now the largest emitter (Source: Our World in Data)
- Opportunities: renewable energy potential, sustainable development investments.
Regional Comparisons:
- Europe:
- Emissions down 25% since 1990 (Source: European Commission)
- Key sectors: energy, industry, agriculture.
- North America:
- Emissions down 14% since 1990 (Source: EPA)
- Key sectors: transportation, electricity, industry.
- Asia:
- Emissions rising rapidly, dominated by China and India.
- Key sectors: energy, industry, transportation.
- Latin America:
- Lower emissions compared to other regions.
- High potential for renewable energy (solar, wind).
- Africa:
- Lowest emissions but expected to rise with development.
- Focus on adaptation and resilience to climate impacts.
Data Sources:
- Our World in Data: https://ourworldindata.org/co2-and-greenhouse-gas-emissions
- Global Carbon Project: https://www.globalcarbonproject.org/
- International Energy Agency (IEA): https://www.iea.org/
- World Bank: https://data.worldbank.org/
- European Commission: https://ec.europa.eu/eurostat
- Environmental Protection Agency (EPA): https://www.epa.gov/
Carbon Footprint by Region: Statistics Table
| Region | Total CO2 Emissions (2022) | Change Since 1990 | Key Sectors | Renewable Energy Potential | Challenges |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Global | 36.1 GtCO2 | +11% | Energy, Industry, Transport | High | Urgent need for emissions reduction |
| Developed | 10.7 GtCO2 | -11% | Energy, Industry, Agriculture | Moderate | Decoupling emissions from economic growth |
| North America | 8.9 GtCO2 | -14% | Transport, Electricity, Industry | High | Persistent emissions from transportation |
| Europe | 3.6 GtCO2 | -25% | Energy, Industry, Agriculture | High | Maintaining emissions reduction momentum |
| Asia | 17.9 GtCO2 | +80% | Energy, Industry, Transport | High | Rapid economic growth driving emissions |
| China | 9.9 GtCO2 | +130% | Energy, Industry, Transport | High | Need for clean energy transition |
| Latin America | 2.1 GtCO2 | +57% | Energy, Industry, Agriculture | Very High | Balancing development with emissions reduction |
| Africa | 1.3 GtCO2 | +80% | Energy, Industry, Agriculture | Very High | Prioritizing adaptation and resilience |
Notes:
- Data for total CO2 emissions is from IEA (2022).
- Change since 1990 is based on estimates from various sources.
- Key sectors are indicative and may vary within each region.
- Renewable energy potential is a general assessment and subject to specific regional conditions.
- Challenges are not exhaustive and vary in their urgency and complexity.
Conclusion The Rising of Carbon Footprint By Region
Conclusion: The Rising Tide, Not Yet an Uncontrollable Wave
The rising carbon footprint across regions paints a worrying picture, but it's not an inevitable fate. While global emissions continue to climb, important insights emerge through a regional lens:
Developed nations: Showing progress through declining emissions, demonstrating the potential for significant reductions. However, challenges like "offshoring" emissions remain.
Developing nations: Facing increasing emissions due to rapid growth, but renewable energy potential and sustainable development pathways offer hope. Developed nations have a historical responsibility to support these efforts.
Regional nuances: Diverse landscapes with unique challenges and opportunities. Latin America's renewable potential and Southeast Asia's green infrastructure investments showcase promising trends.
Shared responsibility: Collective action is crucial. Individual choices like sustainable habits and systemic changes like carbon pricing and clean energy investments are both vital.
Looking ahead: The future is not predetermined. By acknowledging regional variations, understanding challenges and opportunities, and embracing collective responsibility, we can turn the tide towards a low-carbon future. It will require:
- Stronger international cooperation: Developed nations supporting sustainable development in emerging economies.
- Ambitious climate targets: All regions setting and achieving aggressive emissions reduction goals.
- Technological advancements: Accelerating the development and deployment of clean energy technologies.
- Individual action: Everyone taking steps to reduce their carbon footprint.
The rising carbon footprint may seem daunting, but remember, it's not an unstoppable wave. Through collective action, informed by regional insights and driven by a shared sense of responsibility, we can chart a course for a more sustainable future for all.