What is Reneweble Energy Meaning?
Renewable energy refers to any form of energy that is derived from natural sources and can be replenished over time.
This includes sources such as sunlight, wind, water, geothermal heat, and organic matter. Unlike non-renewable energy sources, such as fossil fuels, renewable energy sources are constantly available and can be replenished with the right technology and infrastructure.
Renewable energy is an essential component of the transition to a sustainable future, as it reduces reliance on finite resources and mitigates the negative impacts of climate change. While renewable energy technologies are still developing, they offer promising solutions for a cleaner and more resilient energy future.
Renewable energy benefits
Renewable energy offers numerous benefits that make it a key component of a sustainable future. One of the primary benefits of renewable energy is that it is clean and emits little to no greenhouse gases, reducing the negative impact of energy production on the environment. It also reduces reliance on finite resources, providing a more resilient energy system. Additionally, renewable energy can be harnessed locally, reducing dependence on long-distance energy transmission and strengthening energy security.
Renewable energy sources can also provide economic benefits, such as creating jobs in the renewable energy industry and stimulating local economies. Another advantage of renewable energy is that it can increase energy access in remote and underserved areas, providing a more equitable distribution of energy resources.
Furthermore, renewable energy sources can offer cost savings over time, as the technology becomes more efficient and the infrastructure is developed. Overall, renewable energy provides a range of benefits that can improve energy security, protect the environment, and foster economic growth.
What does net zero carbon mean
Net zero carbon refers to the state in which the amount of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gas emissions released into the atmosphere is balanced by the amount removed from the atmosphere. This can be achieved through a combination of reducing greenhouse gas emissions and implementing carbon removal techniques, such as reforestation or carbon capture and storage.
The goal of net zero carbon is to achieve a balance between emissions and removal, so that the overall impact on the climate is neutral. This is a critical target in the fight against climate change, as it reduces the amount of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere and mitigates the negative impacts of climate change.
Achieving net zero carbon requires a concerted effort from individuals, businesses, and governments to reduce emissions, invest in renewable energy and carbon removal technologies, and transition to more sustainable practices.
The term "Net Zero Carbon" has gained popularity in recent years, reflecting the growing urgency of addressing climate change and reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
While the concept of achieving carbon neutrality has been discussed for several decades, the specific term "Net Zero Carbon" gained traction in the 2010s. The term was popularized by the Paris Agreement, a landmark international agreement on climate change signed in 2015, which set a goal of limiting global temperature increase to well below 2°C above pre-industrial levels and pursuing efforts to limit the temperature increase to 1.5°C.
The Paris Agreement called for global greenhouse gas emissions to reach net zero in the second half of the 21st century, and the term "Net Zero Carbon" has since become a widely recognized and used term in public discourse, policy discussions, and the energy sector.
When did the term renewable energy begin to be used?
The term renewable energy has been in use for several decades, with its origins dating back to the early 1970s. The term was popularized during the oil crisis of the 1970s, when there was a global push to find alternative energy sources due to concerns about energy security and dependence on finite resources. As a result, renewable energy became a key focus for governments, research institutions, and the energy industry.
The concept of renewable energy has evolved over time, with advances in technology and changes in policy and public awareness contributing to the development of the field. Today, renewable energy is a vital component of the transition to a more sustainable future, and the term is widely recognized and used across the energy sector and in public discourse.
Who popularized the term of renewable energy
The term "renewable energy" was not popularized by any one individual, but rather emerged as a result of the growing awareness and concern over finite resources and energy security in the 1970s. The oil crisis of the early 1970s led to a global push for alternative energy sources, and renewable energy emerged as a key focus for governments, research institutions, and the energy industry.
As the importance of renewable energy sources became more widely recognized, the term "renewable energy" gained popularity and became more widely used in public discourse. Today, the term is widely recognized and used across the energy sector and in public discourse, reflecting the growing importance of renewable energy in the transition to a more sustainable future.

What are the benefits of renewable energy against climate change?
Renewable energy can have a significant positive impact on climate change. This is because renewable energy sources, such as wind, solar, hydro, geothermal, and biomass, emit little to no greenhouse gas emissions during operation. As a result, increasing the use of renewable energy can help to reduce the amount of greenhouse gases being emitted into the atmosphere, which are the primary cause of climate change.
In addition to reducing greenhouse gas emissions, renewable energy can also help to reduce air pollution and improve public health, as many fossil fuel sources of energy are also significant sources of air pollutants such as particulate matter and nitrogen oxides.
However, it is important to note that the production and installation of renewable energy systems, such as solar panels and wind turbines, can have some environmental impacts, including land use changes and the use of certain materials in production. It is important to minimize these impacts and ensure that renewable energy development is done in a sustainable and responsible manner.
Who regulates the Renewable Energy Program around the world
There is no single world organization that regulates renewable energy, but there are several international organizations and initiatives that promote renewable energy and provide guidance and support for its development.
One of the most important is the International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA), which is an intergovernmental organization that promotes the widespread adoption and sustainable use of renewable energy worldwide. IRENA supports the development of policies, frameworks, and initiatives to promote renewable energy, and provides technical assistance, capacity building, and knowledge sharing to member countries.
What is IRENA
The International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA) is an intergovernmental organization that was founded in 2009 with the goal of promoting the widespread adoption and sustainable use of renewable energy worldwide.
The organization is headquartered in Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, and has 165 member countries as of 2023. IRENA supports the development of policies, frameworks, and initiatives to promote renewable energy, and provides technical assistance, capacity building, and knowledge sharing to member countries.
The agency conducts research, analysis, and provides advice on renewable energy technologies, and works to build partnerships and collaborations to advance renewable energy globally. IRENA has played a leading role in the international effort to transition to a more sustainable energy future and has been instrumental in driving the growth and development of renewable energy technologies and markets worldwide.
Other organizations that promote renewable energy include the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC), the International Energy Agency (IEA), and the Global Wind Energy Council (GWEC). Additionally, many countries have their own regulatory bodies and policies to promote renewable energy, such as the US Department of Energy and the European Union's Renewable Energy Directive.
What is UNFCCC
The United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) is an international treaty that was established in 1992 with the goal of addressing the problem of global climate change.
The treaty was developed in response to growing concerns about the impacts of rising greenhouse gas emissions on the environment, and the potential consequences for human health, economies, and ecosystems.
The UNFCCC sets out a framework for global cooperation to address climate change, and aims to stabilize greenhouse gas concentrations in the atmosphere at a level that would prevent dangerous anthropogenic interference with the climate system. The UNFCCC has been instrumental in the development of international climate agreements, such as the Paris Agreement, which set the goal of limiting global temperature increase to well below 2°C above pre-industrial levels and pursuing efforts to limit the temperature increase to 1.5°C.
The UNFCCC also hosts annual Conferences of the Parties (COPs), which bring together representatives from countries, civil society, and the private sector to discuss and advance efforts to address climate change.
What is IEA
The International Energy Agency (IEA) is an intergovernmental organization that was established in 1974 with the aim of promoting energy security and sustainable energy policies.
The IEA is headquartered in Paris, France and has 30 member countries as of 2023. The organization conducts research, analysis, and provides advice on energy policy, including renewable energy, energy efficiency, and energy security.
The IEA also plays a key role in providing energy data and statistics, and tracking global trends in energy consumption and production. In addition, the IEA provides technical assistance, capacity building, and knowledge sharing to member countries to support the development and implementation of sustainable energy policies.
The IEA has been influential in shaping international energy policy, and has been a strong advocate for the development and deployment of renewable energy technologies as a key strategy to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and address climate change. is
What is UNFCCC
The United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) is an international treaty that was established in 1992 with the goal of addressing the problem of global climate change.
The treaty was developed in response to growing concerns about the impacts of rising greenhouse gas emissions on the environment, and the potential consequences for human health, economies, and ecosystems. The UNFCCC sets out a framework for global cooperation to address climate change, and aims to stabilize greenhouse gas concentrations in the atmosphere at a level that would prevent dangerous anthropogenic interference with the climate system.
The UNFCCC has been instrumental in the development of international climate agreements, such as the Paris Agreement, which set the goal of limiting global temperature increase to well below 2°C above pre-industrial levels and pursuing efforts to limit the temperature increase to 1.5°C. The UNFCCC also hosts annual Conferences of the Parties (COPs), which bring together representatives from countries, civil society, and the private sector to discuss and advance efforts to address climate change.
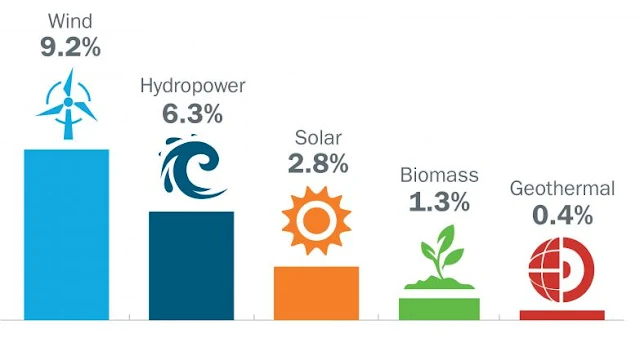
Types Of Renewable Energy
Renewable energy is a crucial aspect of the transition to a sustainable future. There are several types of renewable energy sources, including solar, wind, hydro, geothermal, and biomass.
Percentage of renewable energy users in the world
The percentage of renewable energy users in the world has been steadily increasing in recent years, but the exact figure varies depending on how it is measured. According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), renewable energy sources accounted for approximately 29% of the world's electricity generation in 2020. This includes sources such as hydropower, wind, solar, bioenergy, and geothermal power.
In terms of total final energy consumption, which includes not just electricity but also transportation and heating, the share of renewable energy is lower. According to the Renewables 2021 Global Status Report, published by the Renewable Energy Policy Network for the 21st Century (REN21), renewables accounted for around 11.2% of global final energy consumption in 2019.
It's worth noting that the percentage of renewable energy use varies widely by country and region. Some countries, such as Iceland and Norway, are already largely powered by renewable energy, while others are just beginning to scale up their use of clean energy sources. In addition, the percentage of renewable energy use is expected to continue to grow in the coming years, as more countries set ambitious renewable energy targets and investments in clean energy continue to increase.
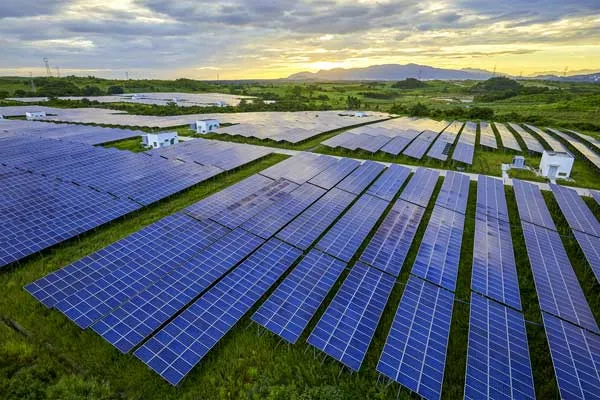

Solar energy
Solar energy is a form of renewable energy that harnesses the power of the sun to generate electricity. This is done through the use of photovoltaic cells, which convert sunlight into electrical energy. It is a popular form of renewable energy due to its widespread availability and the ability to install solar panels on rooftops and other locations.
The World's Largest Solar Energy Project
The world's largest solar energy project is currently the Noor Abu Dhabi Solar Plant, which is located in the United Arab Emirates. The plant has a total capacity of 1.177 GW and covers an area of 8 square kilometers, making it the largest single-site solar project in the world. The Noor Abu Dhabi Solar Plant consists of more than 3.2 million solar panels, which are arranged in long rows and capture the sun's energy to produce electricity.
The plant began operations in April 2019 and is expected to produce enough clean energy to power 90,000 households in the UAE. The project is a joint venture between the Abu Dhabi Power Corporation and a consortium of companies, including China's JinkoSolar and France's EDF Renewables. The Noor Abu Dhabi Solar Plant is a significant milestone in the development of solar energy, and demonstrates the potential of renewable energy sources to meet growing energy demand while reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
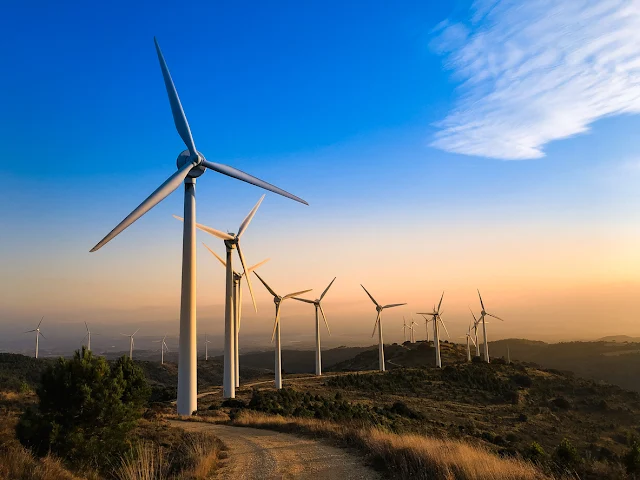

Wind energy
Wind energy is another type of renewable energy that utilizes the power of wind to generate electricity. This is achieved through the use of wind turbines, which capture the energy of the wind and convert it into electrical energy. It is a particularly useful form of renewable energy in areas with high wind speeds.
The World's Largest Wind Energy Project
The world's largest wind energy project is currently the Gansu Wind Farm, which is located in China. The wind farm has a total installed capacity of over 20 GW and covers an area of more than 70,000 hectares. The project consists of multiple wind farms located across the Gansu province in northwestern China, and includes both onshore and offshore wind turbines. The Gansu Wind Farm was developed over several phases, with the first phase beginning in 2008, and was completed in 2019.
The project is part of China's efforts to transition to a low-carbon economy and reduce its dependence on fossil fuels. The Gansu Wind Farm has the potential to generate clean energy to power millions of homes, and is a significant step towards achieving China's goal of reaching peak carbon emissions by 2030 and achieving carbon neutrality by 2060. The success of the Gansu Wind Farm has also led to the development of other large-scale wind energy projects in China and other countries around the world.
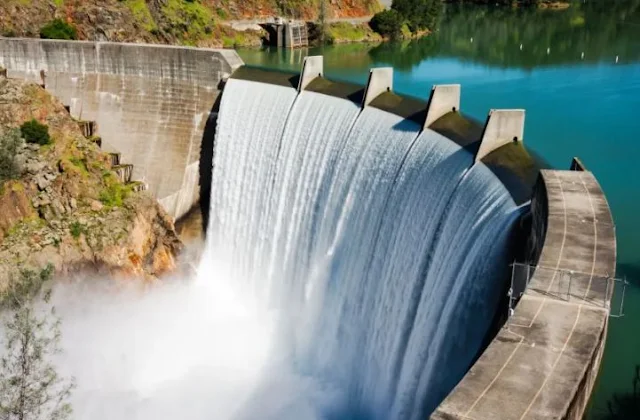

Hydro energy
Hydro energy, also known as hydropower, is a type of renewable energy that harnesses the power of moving water to generate electricity. This is done through the use of dams and turbines, which convert the energy of falling water into electrical energy.
The world's largest hydro energy
The world's largest hydro energy project is currently the Three Gorges Dam, which is located in China. The dam spans the Yangtze River and has a total installed capacity of 22.5 GW, making it the largest power station in the world. Construction of the dam began in 1994 and was completed in 2012.
The Three Gorges Dam is a major source of clean energy for China, producing about 100 billion kilowatt-hours of electricity each year, which is equivalent to burning 40 million tonnes of coal. In addition to providing clean energy, the dam also serves to regulate the flow of the Yangtze River, control floods, and improve navigation in the area. However, the construction of the dam has also been controversial due to its impact on the local environment and displacement of thousands of people living in the area.
Despite these challenges, the Three Gorges Dam remains a significant example of large-scale hydroelectric power, and has inspired the development of other large hydro projects around the world.

Geothermal energy
Geothermal energy is a form of renewable energy that utilizes the heat from within the earth to generate electricity. This is achieved through the use of geothermal power plants, which tap into natural geothermal reservoirs to generate electricity.
The World's Largest Geothermal energy Energy Project
The world's largest geothermal energy project is currently the Geysers, which is located in California, USA. The Geysers is a complex of 22 geothermal power plants with a total installed capacity of 1.5 GW, making it the largest geothermal power installation in the world. The project utilizes the natural geothermal resources in the area to generate electricity by tapping into the steam and hot water found beneath the earth's surface.
The Geysers began operations in the 1960s, and has been in continuous use since then. It is estimated that the project generates enough electricity to power about 725,000 homes, and provides about 60% of the renewable energy produced in California. The Geysers has also been instrumental in the development of geothermal energy around the world, and has served as a model for other geothermal projects in countries such as Iceland, Indonesia, and Kenya.
The use of geothermal energy is a promising solution for the transition to a low-carbon economy, as it is a reliable and sustainable source of clean energy that can be harnessed without producing greenhouse gas emissions.

Biomass energy
Biomass energy is a type of renewable energy that is produced from organic matter, such as wood chips, crop residues, and animal waste. This organic matter is burned to generate heat, which is then used to produce electricity. It is a particularly useful form of renewable energy in areas with a lot of agricultural waste.
The World's Largest Biomass Energy Project
The world's largest biomass energy project is currently the Drax Power Station, which is located in North Yorkshire, England. The power station has a total installed capacity of 3.9 GW, and generates about 12% of the UK's renewable energy. The project utilizes biomass fuel, primarily wood pellets, to generate electricity. The wood pellets are sourced from sustainably managed forests in the United States, Canada, and Europe, and are transported to the Drax Power Station by ship.
The biomass is then burned in specially designed boilers to produce steam, which drives turbines to generate electricity. The project has been successful in reducing the carbon footprint of the UK's energy sector, as the use of biomass is considered to be carbon-neutral, since the carbon emissions from burning the wood pellets are offset by the carbon absorbed during the growth of the trees.
The Drax Power Station is a significant example of the potential of biomass as a renewable energy source, and has inspired the development of other biomass projects around the world. However, the sustainability of biomass as a renewable energy source remains a subject of debate, as the sourcing and transportation of biomass can have a significant impact on the environment.
Is Nuclear Fusion energy categorized as renewable energy?
Nuclear fusion energy is often considered as a potential source of renewable energy, but it is not currently considered a mature renewable energy technology. Unlike nuclear fission, which is used in most nuclear power plants today, nuclear fusion does not produce nuclear waste or greenhouse gas emissions, and it relies on abundant fuel sources, such as hydrogen.
However, nuclear fusion is still a developing technology, and the practical implementation of nuclear fusion for energy generation remains a significant technical challenge. There are currently several research programs and projects around the world working on developing nuclear fusion as a viable source of energy, and if successful, it has the potential to play a significant role in meeting the world's energy demands in a sustainable way.
So while nuclear fusion energy is not yet considered a mature renewable energy technology, it holds promise as a potentially renewable and clean energy source in the future.
Overall, each of these renewable energy sources has unique benefits and challenges, and they are all important in the transition to a more sustainable future.
Leading countries in implementing Renewable Energy
There are several countries around the world that have made significant progress in implementing renewable energy.
Here are a few examples:
China - China is the world's largest investor in renewable energy, and has made significant investments in wind and solar power in recent years. It has also set ambitious targets for increasing the share of renewable energy in its energy mix.
Germany - Germany has made significant investments in renewable energy, particularly in solar power. It has also implemented policies to encourage the deployment of renewable energy technologies, such as feed-in tariffs and net metering.
United States - The United States has made significant progress in deploying renewable energy, particularly in wind and solar power. It has also implemented policies to encourage the adoption of renewable energy technologies, such as tax incentives and renewable portfolio standards.
India - India is rapidly increasing its use of renewable energy, particularly in solar power. It has set ambitious targets for increasing the share of renewable energy in its energy mix, and has implemented policies to encourage the deployment of renewable energy technologies.
Denmark - Denmark has long been a leader in renewable energy, particularly in wind power. It has set ambitious targets for increasing the share of renewable energy in its energy mix, and has implemented policies to encourage the deployment of renewable energy technologies.
These are just a few examples of the leading countries in implementing renewable energy. Other countries that have made significant progress in this area include Spain, Italy, France, and Brazil, among others.

The leading company in the application of Renewable Energy
There are several companies around the world that are leaders in the application of renewable energy technologies.
Here are a few examples:
Tesla - Tesla is a US-based company that specializes in electric vehicles and renewable energy solutions. The company is a leading manufacturer of electric cars and energy storage systems, and also offers solar panels and solar roofs for residential and commercial customers.
Vestas - Vestas is a Danish company that is one of the world's leading manufacturers of wind turbines. The company has installed more than 117 GW of wind power capacity in over 80 countries, and is known for its innovative wind turbine designs.
Enel - Enel is an Italian multinational energy company that is one of the world's largest operators of renewable energy plants. The company has a significant presence in wind and solar power, and has set ambitious targets for increasing its renewable energy capacity in the coming years.
Siemens Gamesa - Siemens Gamesa is a Spanish-German wind turbine manufacturer that is one of the world's largest suppliers of wind turbines. The company has installed more than 100 GW of wind power capacity in over 90 countries, and is known for its high-performance wind turbine designs.
Canadian Solar - Canadian Solar is a Canadian company that is one of the world's leading manufacturers of solar panels. The company has a significant presence in the global solar market, and offers a range of solar solutions for residential, commercial, and utility-scale customers.
These are just a few examples of the leading companies in the application of renewable energy technologies. Other companies that have made significant contributions to the renewable energy sector include First Solar, General Electric, and SunPower, among others.
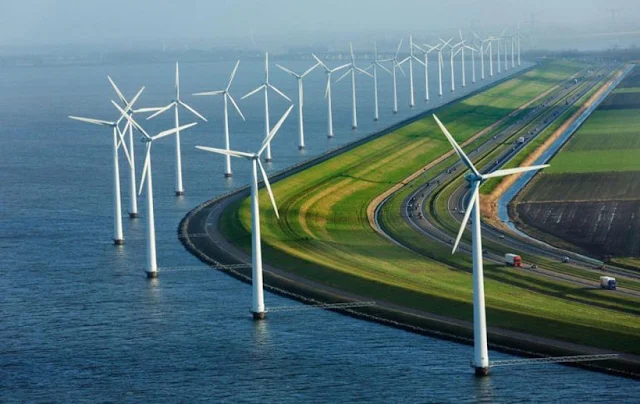

A leading city in the application of renewable energy
There are several cities around the world that are leading the way in the application of renewable energy technologies.
Here are a few examples:
Copenhagen, Denmark - Copenhagen has set ambitious goals to become carbon neutral by 2025, and has made significant investments in wind power and district heating systems. The city also has a large number of bike lanes and pedestrian-friendly areas, which helps reduce carbon emissions from transportation.
Reykjavik, Iceland - Reykjavik is a leader in geothermal energy, with almost 100% of its heating needs supplied by geothermal sources. The city has also invested in a network of electric vehicle charging stations and is working towards becoming carbon neutral by 2040.
San Francisco, USA - San Francisco has set a goal to become 100% reliant on renewable energy by 2030, and has made significant investments in solar and wind power. The city has also implemented policies to encourage the adoption of electric vehicles and energy-efficient buildings.
Munich, Germany - Munich is a leader in solar power, with a significant number of rooftop solar installations and solar-powered public transportation. The city has also implemented policies to encourage the adoption of energy-efficient buildings and has set ambitious goals to reduce its carbon emissions.
Masdar City, UAE - Masdar City is a planned sustainable city located in Abu Dhabi, UAE. The city is powered entirely by renewable energy, and is home to a number of innovative renewable energy projects, including the world's largest concentrated solar power plant.
These are just a few examples of cities that are leading the way in the application of renewable energy technologies. Other cities that have made significant progress in this area include Vancouver, Canada; Barcelona, Spain; and Adelaide, Australia, among others.

Can the net zero carbon target be achieved?
Yes, achieving net zero carbon emissions is technically feasible, but it will require a significant and sustained effort from governments, businesses, and individuals around the world.
The technologies to reduce greenhouse gas emissions already exist, and further advancements in renewable energy, energy efficiency, and carbon capture and storage could help accelerate progress towards achieving net zero emissions.
However, achieving net zero carbon will also require significant changes in our societal and economic systems, including transitioning away from fossil fuels and scaling up renewable energy sources, improving energy efficiency in buildings and transportation, and making changes to land use and agriculture practices. It will also require political will and policy support, including carbon pricing mechanisms, incentives for clean energy investment, and regulations to phase out the use of fossil fuels.
Overall, achieving net zero carbon emissions will be a significant challenge, but with collective effort and commitment, it is possible to achieve and could help prevent the worst impacts of climate change.
Conclusion Outlook of Renewable Energy
Renewable energy is a rapidly growing and vital part of our world's energy mix. With its many benefits, including reducing carbon emissions and improving energy security, governments, businesses, and individuals around the world are increasingly turning to renewable energy as a way to power our world sustainably.
From wind and solar power to geothermal and hydropower, there are a variety of renewable energy sources that are being harnessed in innovative and exciting ways. As we move forward, it is clear that renewable energy will continue to play a critical role in meeting our energy needs while helping to protect our planet for generations to come.
As the world increasingly recognizes the urgent need to transition to cleaner energy sources, renewable energy is emerging as a key solution for addressing our energy needs while reducing greenhouse gas emissions and other environmental impacts.
With ongoing technological advancements and increased investments, renewable energy is poised to play an ever-growing role in powering our world, creating jobs, and driving economic growth, while also helping to mitigate the impacts of climate change. As we continue to make progress towards a more sustainable energy future, it is clear that renewable energy will play a critical role in shaping the future of our plan

